108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

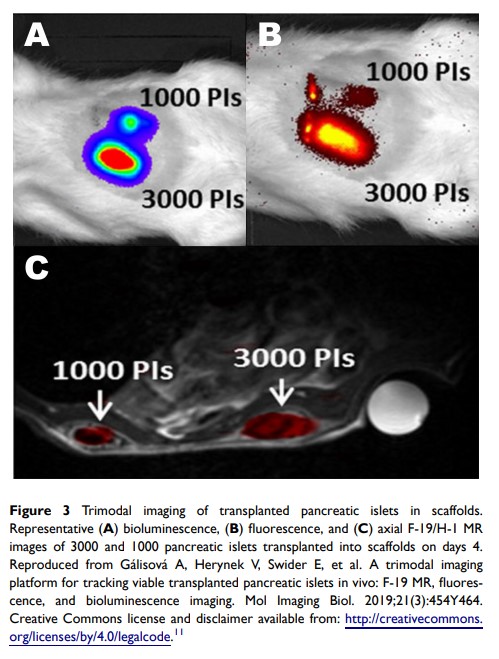
胰岛体内移植成像
Authors Zheng L, Wang Y, Yang B, Zhang B, Wu Y
Received 17 May 2020
Accepted for publication 29 July 2020
Published 23 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3301—3311
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S263253
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Juei-Tang Cheng
Abstract: Although islet transplantation plays an effective and powerful role in the treatment of diabetes, a large amount of islet grafts are lost at an early stage due to instant blood-mediated inflammatory reactions, immune rejection, and β-cell toxicity resulting from immunosuppressive agents. Timely intervention based on the viability and function of the transplanted islets at an early stage is crucial. Various islet transplantation imaging techniques are available for monitoring the conditions of post-transplanted islets. Due to the development of various imaging modalities and the continuous study of contrast agents, non-invasive islet transplantation imaging in vivo has made great progress. The tracing and functional evaluation of transplanted islets in vivo have thus become possible. However, most studies on contrast agent and imaging modalities are limited to animal experiments, and long-term toxicity and stability need further evaluation. Accordingly, the clinical application of the current achievements still requires a large amount of effort. In this review, we discuss the contrast agents for MRI, SPECT/PET, BLI/FI, US, MPI, PAI, and multimodal imaging. We further summarize the advantages and limitations of various molecular imaging methods.
Keywords: islet transplantation, imaging modality, non-invasive imaging, multimodal imaging, contrast agent