108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

前折叠素及其亚基在肿瘤中的作用及其在纳米医学中的应用前景
Authors Mo S, Zhao H, Tian Y, Zhao HL
Received 1 July 2020
Accepted for publication 24 August 2020
Published 23 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8847—8856
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S270237
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
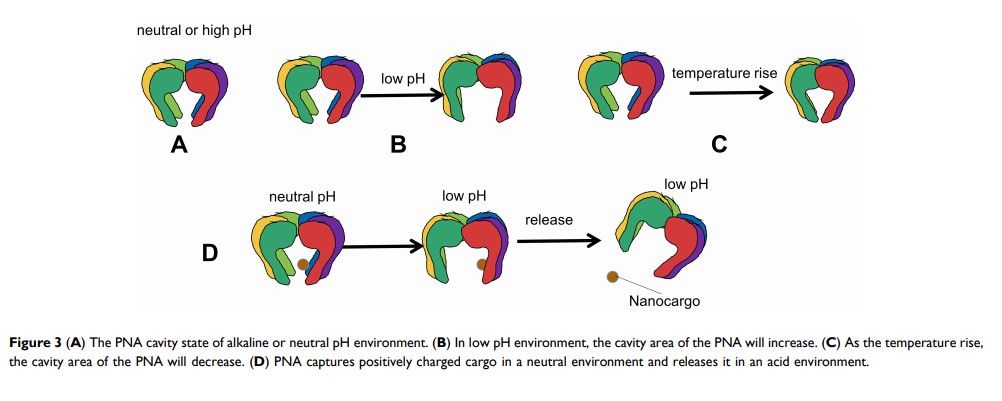
Abstract: Prefoldin (PFDN) is a hexameric chaperone complex that is widely found in eukaryotes and archaea and consists of six different subunits (PFDN1-6). Its main function is to transfer actin and tubulin monomers to the eukaryotic cell cytoplasmic chaperone protein (c-CPN) specific binding during the assembly of the cytoskeleton, to stabilize the newly synthesized peptides so that they can be folded correctly. The current study found that each subunit of PFDN has different functions, which are closely related to the occurrence, development and prognosis of tumors. However, the best characteristics of each subunit have not been fully affirmed. The connection between research and tumors can change the understanding of PFDN and further extend its potential prognostic role and structural function to cancer research and clinical practice. This article mainly reviews the role of canonical PFDN and its subunits in tumors and other diseases, and discusses the potential prospects of the unique structure and function of PFDN in nanomedicine.
Keywords: prefoldin, disease, tumor, nanomedicine