108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CELSR1 在 miR-199a-5p 的调控下,成为神经胶质瘤的致癌基因
Authors Wang G, Li Y, Zhang D, Zhao S, Zhang Q, Luo C, Sun X, Zhang B
Received 19 April 2020
Accepted for publication 2 July 2020
Published 23 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 8857—8865
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S258835
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
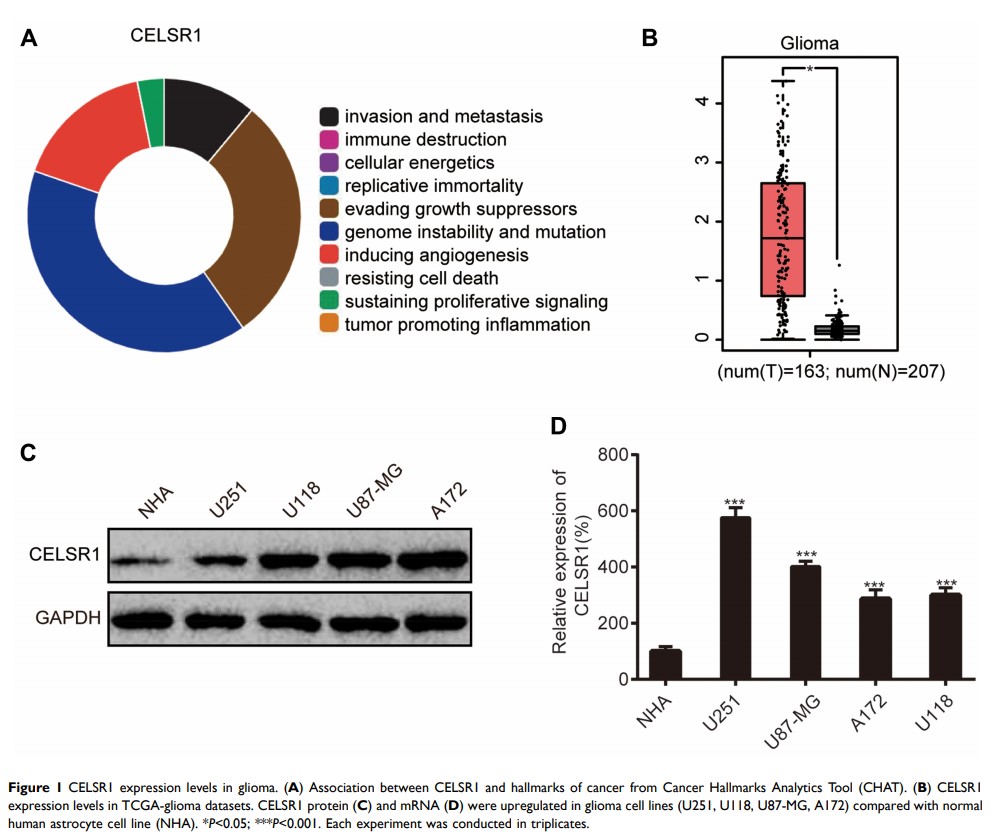
Purpose: This study aimed to elucidate the biological function and upstream regulatory mechanism of CELSR1 in glioma.
Materials and Methods: We evaluated the expression of CELSR1 in glioma by TCGA_GEPIA tool, RT-qPCR, and Western blot assays. CCK-8, wound healing, and transwell invasion assays were, respectively, performed to detect the effect of CELSR1 on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The upstream regulatory miRNAs of CELSR1 were predicted by TargetScan and validated by luciferase activity reporter assay.
Results: CELSR1 is overexpressed in glioma (P < 0.05). CELSR1 promoted glioma cell proliferation, migration and invasion (P < 0.01). CELSR1 was a direct target of miR-199a-5p. miR199a-5p mimics significantly inhibited CELSR1 mRNA and protein expression (P < 0.01). miR199a-5p mimics reversed the effects of CELSR1 on glioma cell behaviors (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: CELSR1 acts as an oncogene promoting glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, which is regulated by miR199a-5p.
Keywords: CELSR1, miR-199a-5p, glioma, proliferation, migration, invasion