108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

旨在用于胃癌干细胞 CD44 和 Gli1 双重靶向的新型治疗性 siRNA 纳米粒子
Authors Yao H, Sun L, Li J, Zhou X, Li R, Shao R, Zhang Y, Li L
Received 27 April 2020
Accepted for publication 7 August 2020
Published 23 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 7013—7034
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S260163
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Purpose: Gastric cancer stem cells (CSCs) are important for the initiation, growth, recurrence, and metastasis of gastric cancer, due to their chemo-resistance and indefinite proliferation. Herein, to eliminate gastric CSCs, we developed novel CSC-targeting glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 (Gli1) small interfering RNA (siRNA) nanoparticles that are specifically guided by a di-stearoyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine- hyaluronic-acid (DSPE-HA) single-point conjugate, as an intrinsic ligand of the CD44 receptor. We refer to these as targeting Gli1 siRNA nanoparticles.
Methods: We used the reductive amination reaction method for attaching amine groups of DSPE to aldehydic group of hyaluronic acid (HA) at the reducing end, to synthesize the DSPE-HA single-point conjugate. Next, targeting Gli1 siRNA nanoparticles were prepared using the layer-by-layer assembly method. We characterized the stem cellular features of targeting Gli1 siRNA nanoparticles, including their targeting efficiency, self-renewal capacity, the migration and invasion capacity of gastric CSCs, and the penetration ability of 3D tumor spheroids. Next, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of the targeting Gli1 siRNA nanoparticles by using in vivo relapsed tumor models of gastric CSCs.
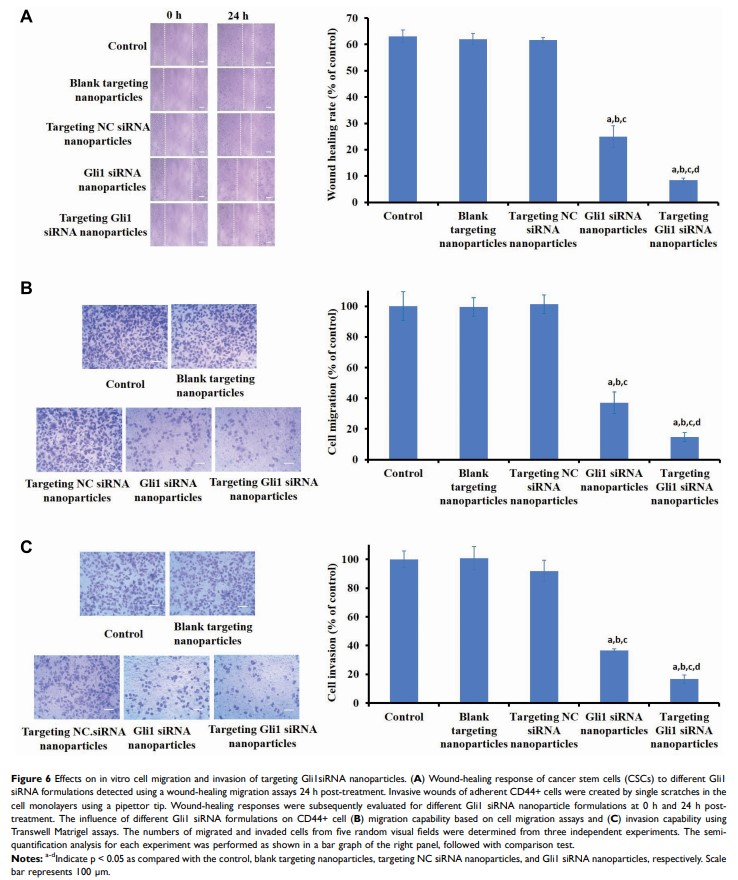
Results: Compared with the multipoint conjugates, DSPE-HA single-point conjugates on the surface of nanoparticles showed significantly higher binding affinities with CD44. The targeting Gli1 siRNA nanoparticles significantly decreased Gli1 protein expression, inhibited CSC tumor spheroid and colony formation, and suppressed cell migration and invasion. Furthermore, in vivo imaging demonstrated that targeting Gli1 siRNA nanoparticles accumulated in tumor tissues, showing significant antitumor recurrence efficacy in vivo.
Conclusion: In summary, our targeting Gli1 siRNA nanoparticles significantly inhibited CSC malignancy features by specifically blocking Hedgehog (Hh) signaling both in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that this novel siRNA delivery system that specifically eliminates gastric CSCs provides a promising targeted therapeutic strategy for gastric cancer treatment.
Keywords: Hedgehog (Hh) pathway, Gli1 siRNA, gastric cancer stem cells, di-stearoyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine-hyaluronic acid (DSPE-HA) single-point conjugate, therapeutic siRNA nanoparticles