108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

FENO 测量技术在预测慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重患者治疗反应中的价值
Authors Zhou A, Zhou Z, Deng D, Zhao Y, Duan J, Cheng W, Liu C, Chen P
Received 22 May 2020
Accepted for publication 31 August 2020
Published 24 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2257—2266
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S263673
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Background: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) has been shown to be a marker of airway inflammation in various pulmonary diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In this study, we assessed the FENO level in patients with acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) and analyzed the predictive value of the FENO level for treatment response.
Methods: Demographic data were collected at admission. FENO, lung function, blood gases, COPD Assessment Test (CAT), and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) scores were measured at admission and on day 7. At the second visit, the patients were asked to report their health status; scores ranged from 1 to 5, representing “much better”, “slightly better”, “no change”, “slightly worse”, and “much worse”, respectively. The treatment response was evaluated based on the patient’s reported health status (responders were those who reported much better and slightly better) and lung function (responders were those who presented an increase in FEV1 over 200 mL).
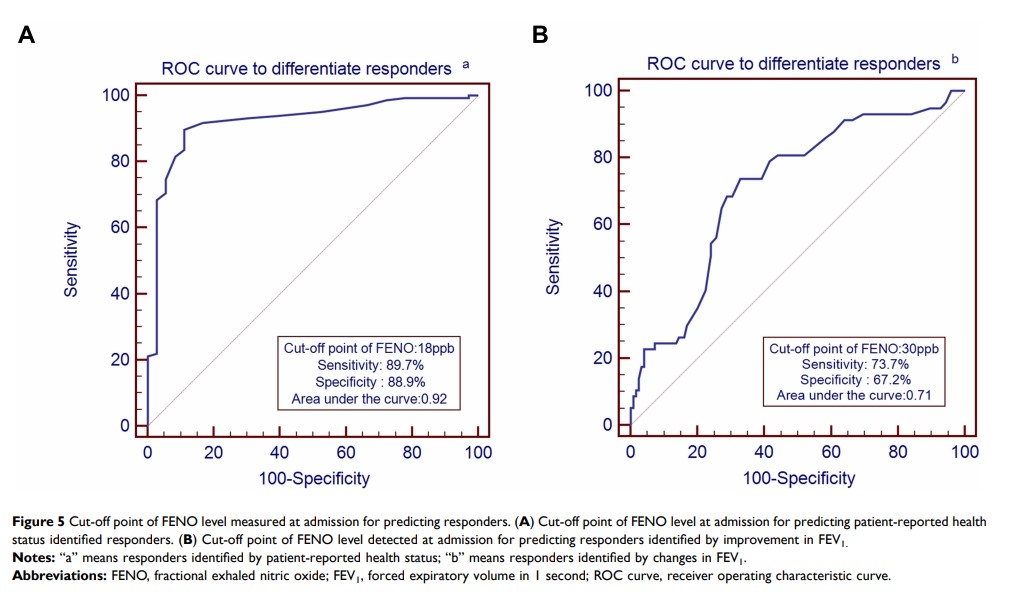
Results: A total of 182 patients were recruited into the analysis. The FENO level positively correlated with an increase in FEV1 and FEV1% (r = 0.291, p < 0.001 and r = 0.205, p = 0.005, respectively), but negatively correlated with a decrease in the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score (r = − 0.197, p = 0.008) and patient-reported health status (rho = − 0.408, p< 0.001). An inverse correlation was observed between FENO concentrations at admission and the length of hospital stay. The cut-off point for differentiating responders, identified by health status, was 18 ppb, with the sensitivity being 89.7% and specificity 88.9%.
Conclusion: FENO levels, determined at hospital admission, are potential to predict the overall treatment response in AECOPD patients, including remission in subjective patient-reported health statuses and, also, improvements in lung function.
Registry Number: ChiCTR-ROC-16,009,087 (http://www.chictr.org.cn/).
Keywords: COPD, exacerbation, FENO, lung function, treatment response