108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在中国工业区,慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重的危险因素:一个多中心横断面研究
Authors Dong H, Hao Y, Li D, Su Z, Li W, Shi B, Gao P
Received 4 July 2020
Accepted for publication 31 August 2020
Published 24 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2249—2256
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S270729
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Background: The exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) seriously affects the patient’s quality of life and prognosis. This multicenter cross-sectional study investigated the characteristics of stable COPD and risk factors for acute exacerbation of COPD (AECOPD) in patients in Changchun, Jilin Province, China.
Methods: The study included 400 outpatients admitted to four secondary hospitals and four tertiary hospitals in Jilin Province from March 2018 to March 2019. Data on the general condition of stable COPD patients, patient self-management, COPD Assessment Test (CAT) scores, number of acute exacerbations in the past 12 months, and medications received during the study period were collected using a questionnaire.
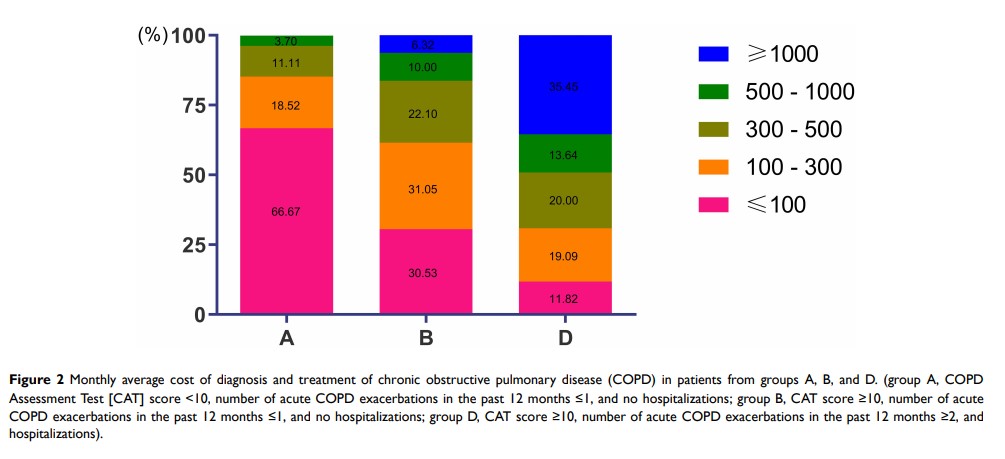
Results: Sociodemographic characteristics and clinical data were obtained from 306 patients, and drug prescription data were obtained from 329 patients. Pearson correlation analysis revealed that CAT scores were positively correlated with the number of acute exacerbations. Age, education level, smoking history, disease duration, number of comorbidities, and the presence of ischemic heart disease (IHD) were associated with AECOPD. Moreover, the level of education, disease duration, and the presence of IHD were independent risk factors for AECOPD. Poor compliance due to the lack of understanding of the disease and the high cost of treatment is a risk factor for AECOPD. In addition, increased air pollution in industrial cities and vitamin D deficiency are closely related to AECOPD.
Conclusion: Low education level, long disease duration, and the presence of IHD may promote the exacerbation and poor control of COPD in patients in Jilin Province.
Keywords: COPD, exacerbation, risk factors, Jilin Province