108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-210 是一种血清生物学标志物,可预测接受射频消融治疗的结肠癌肝转移患者的复发和预后
Authors Zhang Y, Zhou YM, Zhang ZJ, Li X
Received 18 June 2020
Accepted for publication 11 August 2020
Published 25 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9077—9085
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S267731
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Purpose: Hepatic metastasis of colon carcinoma seriously affects the prognosis of patients, and miRNA has attracted much attention in predicting hepatic metastasis of colon carcinoma (CC). This research aimed to explore the predictive role of miR-210 in serum for recurrence and prognosis of CC patients with hepatic metastasis.
Methods: Altogether, 150 patients with liver metastases of CC (research group, RG) and 130 patients with non-metastatic of CC (control group, CG) admitted to People’s Hospital of Deyang City from March 2012 to March 2015 were obtained and their serum was collected. miR-210 in the RG and the CG, and miR-210 in the RG after radiofrequency ablation treatment were detected, the relationship between miR-210 and pathological parameters of CC patients with hepatic metastasis was analyzed, and patients in the RG were followed up for 5 years to analyze the recurrence, overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). The area under the curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was applied to test the predictive value of miR-210. Cox regression was applied to analyze the independent prognostic factors of patients.
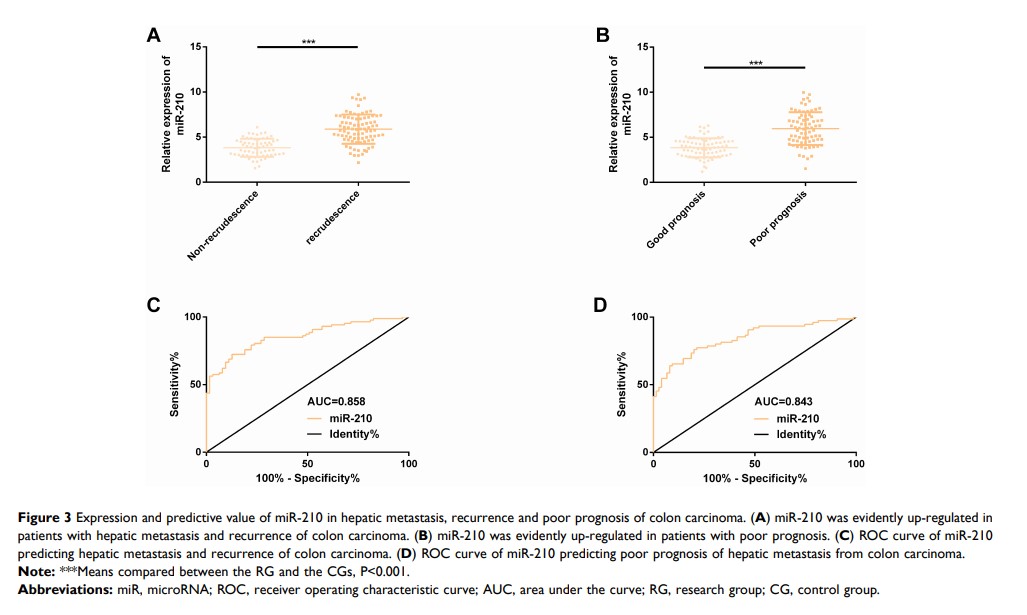
Results: miR-210 in the RG was evidently higher than that in the CG, and AUC for distinguishing hepatic metastasis of CC was 0.907. miR-210 had a close correlation with lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis and pathological differentiation. After treatment, miR-210 in the RG was evidently reduced, and the serum was higher in patients with recurrence and with poor prognosis. AUC for predicting recurrence was 0.858, and AUC for predicting poor prognosis was 0.843. High miR-210 was closely related to lower 5-year OS and DFS and is also an independent prognostic factor affecting patients’ 5-year OS.
Conclusion: miR-210 is enhanced in hepatic metastasis of CC, which is a serological biomarker for predicting recurrence and prognosis of patients with hepatic metastasis of CC after radiofrequency ablation, and has great clinical application value.
Keywords: hepatic metastasis of colon carcinoma, miR-210, radiofrequency ablation, recurrence, prognosis