108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA SNHG14 通过海绵化 miR-382-5p 调节 SPIN1 表达,以促进非小细胞肺癌肿瘤进展
Authors Chen X, Song P, Yao Y, Yang Y
Received 22 February 2020
Accepted for publication 26 June 2020
Published 25 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9113—9123
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S250893
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Rudolph Navari
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung carcinoma. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) small nucleolar RNA host gene 14 (SNHG14 ) was identified to participate in tumor progression. However, the mechanism and functions of SNHG14 were rarely reported in NSCLC progression.
Methods: The relative gene expression was tested by qRT-PCR. Cell viability, apoptosis, migration and invasion were measured by MTT assay, flow cytometry, and transwell migration and invasion assays, respectively. The interactions between miR-382-5p and SNHG14 or SPIN1 were predicted by starBase and confirmed by the dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA pull-down assay. The protein level of SPIN1 was evaluated by Western blot assay.
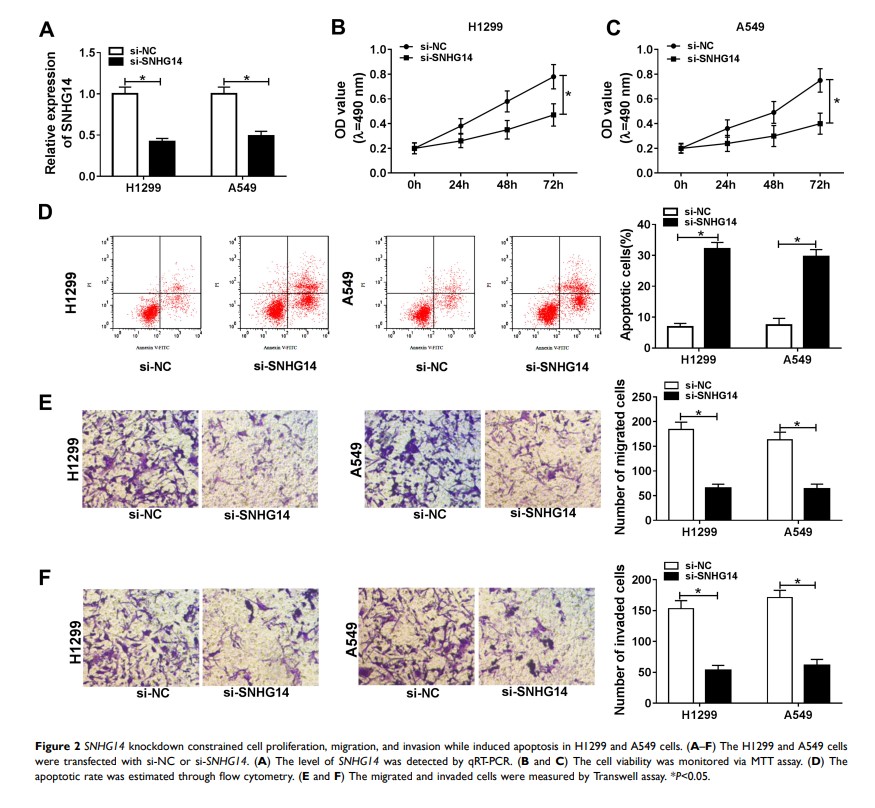
Results: The levels of SNHG14 and SPIN1 were significantly increased, while the level of miR-382-5p was apparently reduced in NSCLC tissues and cells. SNHG14 was verified to sponge miR-382-5p and SPIN1 was identified as a direct target of miR-382-5p . SNHG14 depletion repressed cell viability, migration and invasion, but induced the apoptotic rate by targeting miR-382-5p . miR-382-5p overexpression blocked cell viability, metastasis and promoted cell apoptosis by regulating SPIN1 . SNHG14 silencing down-regulated SPIN1 expression by sponging miR-382-5p .
Conclusion: SNHG14 facilitated NSCLC progression by regulating SPIN1 expression via targeting miR-382-5p .
Keywords: lncRNA SNHG14 , miR-382-5p , SPIN1 , tumor progression, NSCLC