108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

安罗替尼治疗肢端硬纤维瘤病患者的活性和安全性:单一机构的回顾性研究
Authors Zheng C, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Luo Y, Tu C, Min L
Received 6 July 2020
Accepted for publication 2 September 2020
Published 25 September 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3941—3950
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S271008
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Purpose: Desmoid fibromatosis (DF) is an aggressive fibroblastic neoplasm with a high propensity for local recurrence. Although multiple therapeutic modalities seem effective for DF, the standard systemic treatment for symptomatic and progressive DF remains controversial. As targeted therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been recently reported to contribute to the treatment of DF. Thus, the purpose of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of anlotinib, a novel multi-kinase angiogenesis inhibitor, in patients with DF.
Patients and Methods: We retrospectively collected the clinical medical records of patients with extremity DF who received anlotinib between January 2019 and January 2020 in our center. Anlotinib was started with a dose of 8 mg daily and adjusted according to the drug-related toxicity. Tumor response was assessed by the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.1 criteria. Progression-free survival (PFS) was identified as the primary endpoint and analyzed using the Kaplan–Meier method.
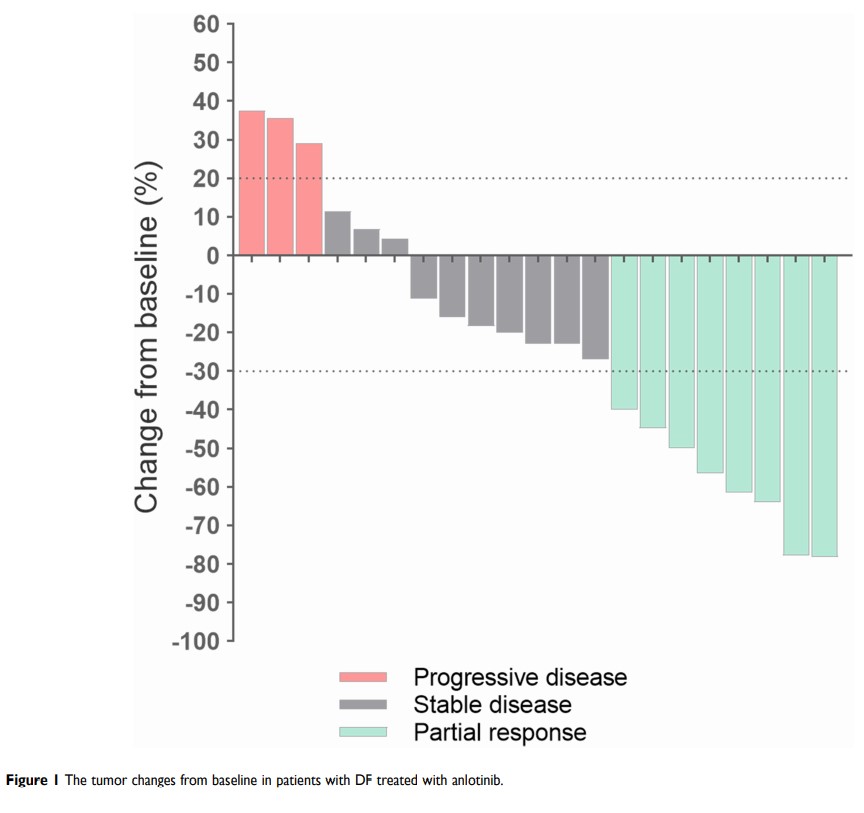
Results: In total, 21 (6 male, 15 female) consecutive patients with DF were enrolled. The median medication time was nine months (Q1, Q3: 7.5, 10.5). None of the patients achieved a complete response, but eight (38.1%) patients achieved a partial response and ten patients (47.6%) achieved disease stability. Three (14%) patients developed progressive disease and the 3-, 6-, and 12-month PFS rates were 95.2%, 90.5%, and 84.0%, respectively. The disease control rate was 86.0% (18/21) and the objective response rate was 38.1% (8/21). Moreover, 15/21 (71.4%) patients achieved a reduction in tumor size, accompanied with a decrease in T2-weighted signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging and clinical benefit.
Conclusion: Anlotinib was effective against DF with an acceptable safety profile, and significantly slowed the disease progression. Further, multicenter studies with a longer follow-up time are needed to characterize fully the clinical application of anlotinib in DF.
Keywords: desmoid fibromatosis, anlotinib, tyrosine kinase inhibitor, targeted therapy