108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

来自怒江藤黄的抗肿瘤呫吨酮通过 PARP,PI3K/AKT/mTOR 和 MAPK/ERK 信号通路抑制人卵巢癌细胞的增殖并诱导细胞凋亡
Authors Tang Z, Lu L, Xia Z
Received 30 April 2020
Accepted for publication 21 August 2020
Published 25 September 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3965—3976
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S258811
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a serious public health concern in the world. It is important to develop novel drugs to inhibit OC.
Purpose: This study investigated the isolation, elucidation, efficiency, molecular docking, and pharmaceutical mechanisms of xanthones isolated from Garcinia nujiangensis .
Methods: Xanthones were isolated, and purified by different chromatography, including silica gel, reversed-phase silica gel (ODS-C18), and semipreparative HPLC, then identified by analysis of their spectral data. Three xanthones were estimated for their efficiency on the human OC cells HEY and ES-2. 2 was found to be the most potent cytotoxic xanthones of those tested. Further, its mechanisms of action were explored by molecular docking, cell apoptosis, and Western blotting analysis.
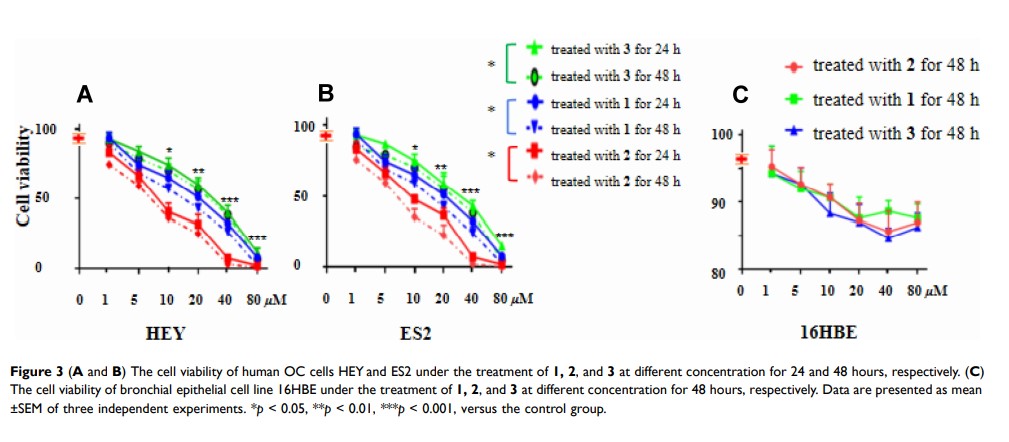
Results: Bioassay-guided fractionation of the fruits of Garcinia nujiangensis led to the separation of a new xanthone named nujiangexanthone G ( 1) and two known xanthones. Among these, isojacareubin ( 2) exhibited the most potent cytotoxic compound against the HEY and ES-2 cell lines. The analysis of Western blot suggested that 2 inhibited OC via regulating the PARP, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and ERK/MAPK signal pathways in the HEY cell lines.
Conclusion: In conclusion, isojacareubin ( 2) might be a potential drug for the treatment of OC.
Keywords: Garcinia nujiangensis , xanthone, ovarian cancer; OC, molecular docking, apoptosis