108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

靶向 PSMA 的可还原裂解超支化聚酰胺-胺基因递送系统用于治疗前列腺癌骨转移
Authors Ye Y, Zhang L, Dai Y, Wang Z, Li C, Peng Y, Ma D, He P
Received 18 June 2020
Accepted for publication 1 September 2020
Published 28 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 7173—7184
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S268398
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Thomas J Webster
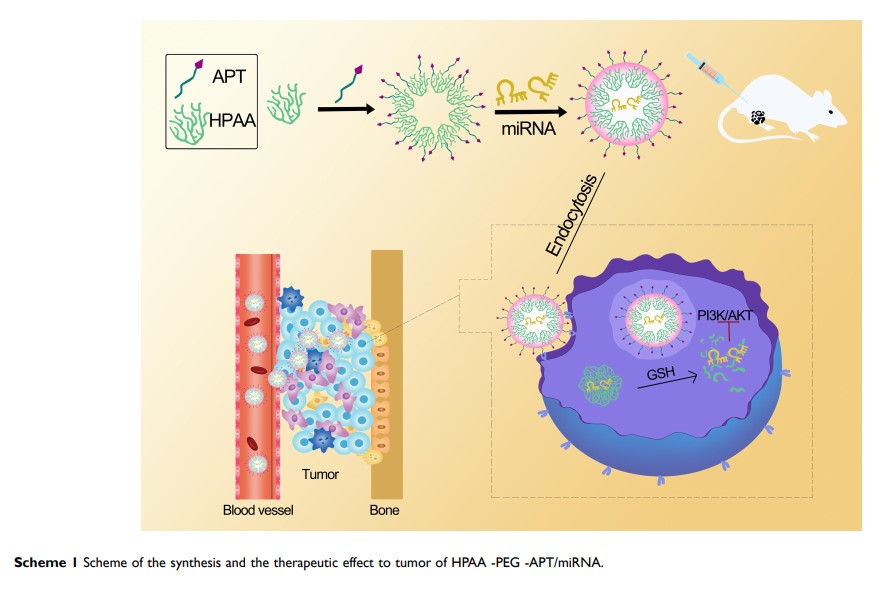
Objective: This study aimed to develop aptamer-anchored hyperbranched poly(amido amine) (HPAA) for the systemic delivery of miRNA-133a-3p and to evaluate its therapeutic potential against bone metastasis of prostate cancer in vivo and in vitro.
Methods: A glutathione (GSH)-responsive cationic HPAA was prepared by the Michael addition reaction. Furthermore, HPAA-PEG was produced by PEGylation, and then the aptamer targeted to prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) was conjugated to the HPAA-PEG. The obtained HPAA-PEG-APT could form nanocomplexes with miRNA-133a-3p through electrostatic adsorption.
Results: The results of immunocytochemistry indicated that the complexes could target PSMA-expressing LNCaP cells. The ability of HPAA-PEG-APT to facilitate the delivery of miRNA-133a-3p into LNCaP cells was proven, and HPAA-PEG-APT/miRNA-133a-3p demonstrated enhanced antitumor activity, lower cytotoxicity and better biocompatibility in vitro. Moreover, in a mouse tibial injection tumor model, the intravenous injection of the HPAA-PEG-APT/miRNA-133a-3p complex significantly inhibited cancer growth and extended the survival time.
Conclusion: This study provided an aptamer-anchored HPAA-loaded gene system to deliver miRNA-133a-3p for better therapeutic efficacy of bone metastasis of prostate cancer.
Keywords: miRNA, aptamer, hyperbranched polyamide amine, bone metastasis, prostate cancer