108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

较高的血管细胞粘附分子 1 与慢性阻塞性肺疾病中不断增加的心血管事件发生风险有关
Authors Li J, Wang Q, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Wan X, Miao C, Zeng Z
Received 28 May 2020
Accepted for publication 6 September 2020
Published 28 September 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 2289—2295
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S264889
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Background: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) is associated with vascular-related inflammation and atherosclerosis. This study aimed to evaluate whether VCAM-1 can be used for an indication of increased risk of CV events in patients with COPD.
Methods: Serum VCAM-1 levels were measured in 163 COPD patients. All COPD patients were prospectively followed up for a median period of 48 months (range=3– 54). Cox proportional hazard analysis was performed to evaluate the prognostic value of serum VCAM-1 for predicting CV events.
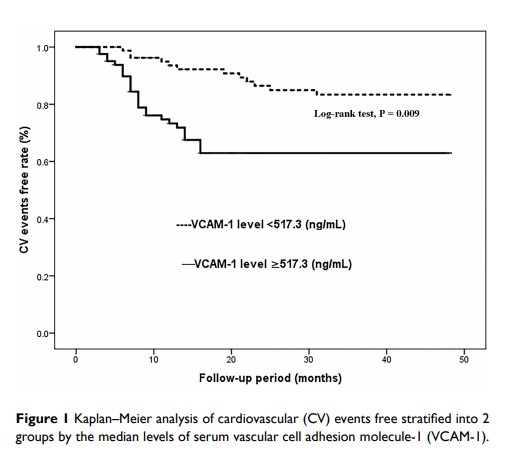
Results: Serum VCAM-1 levels were higher in COPD patients with CV events than in those without CV events (1174.4± 365.3 ng/mL vs 947.8± 293.2 ng/mL; P < 0.001). The logistic regression analysis revealed that serum VCAM-1 (OR=1.750; 95% CI, 1.324– 2.428; P trend= 0.0012) was independently associated with CVD (cardiovascular disease) history after adjusting for age, sex, BMI, current smoker, current drinker, admission systolic and diastolic BP, LVEF and laboratory measurements in patients with COPD at baseline. The Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated that the rate of CV events was higher in COPD patients with serum VCAM-1 levels above the median (517.3 ng/mL) than in those with VCAM-1 levels below the median. The Cox proportional hazard analysis revealed that serum VCAM-1 (HR=2.617; 95% CI, 1.673– 5.328; P trend< 0.001) may be an independent prognostic factor for CV events in the COPD patients.
Conclusion: Our results suggested that serum VCAM-1 was significantly and independently associated with CV events in COPD patients. The inflammatory marker may help clinicians predict CV complications early.
Keywords: vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cardiovascular events, prognostic value