108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血浆中同型半胱氨酸浓度和传统心血管危险因素对新发周围性动脉疾病风险的联合影响
Authors Liu M, Fan F, Liu B, Jia J, Jiang Y, Sun P, He D, Liu J, Li Y, Huo Y, Li J, Zhang Y
Received 12 June 2020
Accepted for publication 28 August 2020
Published 28 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3383—3393
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S267122
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ming-Hui Zou
Purpose: Hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent risk factor for cardio- and cerebrovascular diseases. However, the relationship between plasma homocysteine (Hcy) concentration and peripheral arterial disease (PAD) has not been completely characterized. The aim of the present study was to determine the relationship between plasma Hcy concentration and new-onset PAD and to assess the effects of combinations of Hcy and traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
Patients and Methods: We conducted a prospective community-based cohort study of 3119 Chinese participants who did not have PAD at baseline, with a median follow-up period of 2.30 years. We used multivariate logistic regression models to evaluate the relationship between high Hcy (≥ 10μmol/L) and new-onset PAD. The effects of combinations of high Hcy and traditional cardiovascular risk factors were assessed using logistic regression analysis.
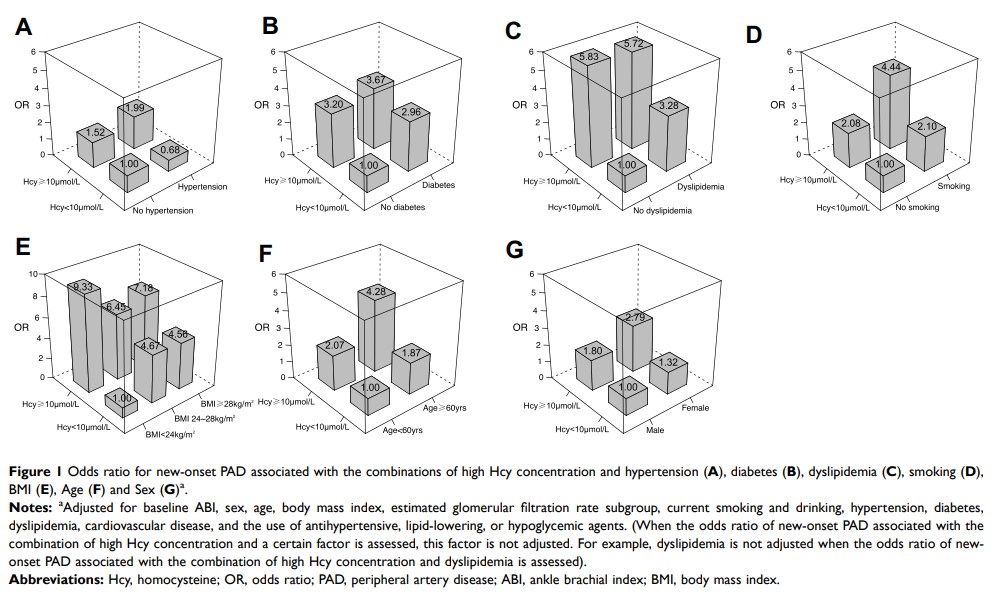
Results: After adjustment for 14 covariates, high Hcy concentration was significantly associated with new-onset PAD (odds ratio [OR]=2.08, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.08– 4.03, P =0.030). Smokers with high Hcy concentration were substantially more likely to have new-onset PAD than non-smokers with normal Hcy concentration (OR=4.44, 95% CI: 1.77– 11.12, P =0.001). The effect of diabetes on PAD became significant when present in combination with high Hcy concentration (OR=3.67, 95% CI: 1.25– 10.80, P =0.018). Participants with both elevated Hcy levels and older age had the highest risk of new-onset PAD (OR=4.28, 95% CI: 1.83– 10.01, P < 0.001). With regard to the joint effect of Hcy and hypertension, dyslipidemia or sex, there was also a trend towards increased risk across four different groups (P for trend=0.026, 0.035, 0.016, respectively).
Conclusion: High plasma Hcy concentration independently predicts the incidence of PAD. Furthermore, there is a joint effect of high Hcy concentration and traditional cardiovascular risk factors such as smoking, diabetes and aging on the incidence of PAD.
Keywords: peripheral arterial disease, atherosclerosis, hyperhomocysteinemia, cohort study, community-based population