108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

microRNA-139-3p 可通过 KDM5B/SOX2 轴和 Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路抑制喉癌细胞的恶性行为
Authors Ma Y, Chen Z, Yu G
Received 22 June 2020
Accepted for publication 15 August 2020
Published 28 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9197—9209
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S268871
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Background: Laryngeal cancer (LCA) is a common head and neck cancer. Lysine demethylase 5B (KDM5B ) knockdown is expected as a new target for cancer prevention. We investigated the molecular mechanism of KDM5B in LCA.
Materials and Methods: The levels of KDM5B , microRNA (miR)-139-3p and high-mobility-group box 2 (SOX2 ) in LCA tissues and cells, normal tissues and cells were detected. The effect of KDM5B on LCA was evaluated. The upstream miR of KDM5B and the downstream gene and pathway of KDM5B were predicted and their effects on LCA were analyzed. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway-specific activator agonist was delivered into LCA cells expressing miR-139-3p mimic to evaluate the role of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
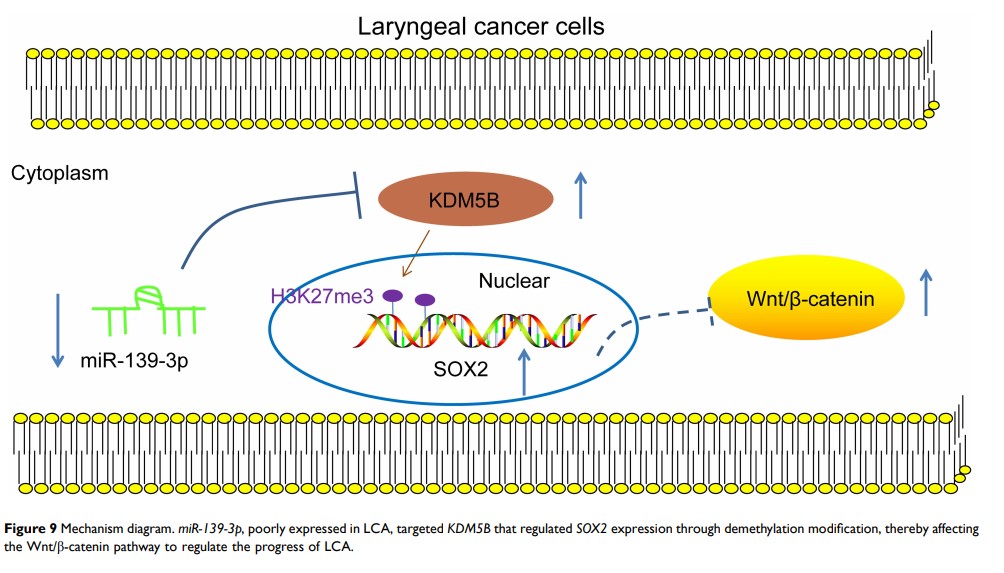
Results: KDM5B was highly expressed in LCA, and inhibition of KDM5B suppressed LCA progression. miR-139-3p , downregulated in LCA tissues, was a regulatory miR of KDM5B . Overexpression of miR-139-3p significantly inhibited the malignant biological behaviors of LCA cells. KDM5B promoted SOX2 expression via histone demethylation. SOX2 was highly expressed in LCA, and overexpression of SOX2 promoted LCA progression by inducing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Activated Wnt/β-catenin pathway attenuated the inhibitory effect of miR-139-3p mimic on the malignant biological behaviors of LCA cells.
Conclusion: miR-139-3p overexpression inhibited LCA development via regulating the KDM5B/SOX2 axis and inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Keywords: laryngeal cancer, microRNA-139-3p , lysine demethylase 5B, high-mobility-group box 2, Wnt/β-catenin pathway