108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

藤黄酸通过 circRNA_ASAP2/miR-33a-5p/CDK7 轴抑制胃癌的进展
Authors Lin D, Lin X, He T, Xie G
Received 28 June 2020
Accepted for publication 27 August 2020
Published 28 September 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9221—9233
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S269768
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) is a major cancer-related mortality disease. Gambogic acid (GA) has been investigated to inhibit cancer progression. In the present study, the molecular mechanism of GA in regulating GC progression was studied.
Methods: The expression levels of circular RNA ASAP2 (circ_ASAP2), miR-33a-5p and cyclin-dependent kinases 7 (CDK7 ) were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase reaction (qRT-PCR). CDK7 protein level was evaluated by Western blot. Cell colony formation assay, 3-(4,5-Dimethylthazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, transwell assay and flow cytometry analysis were employed to reveal the functional effects among circ_ASAP2, miR-33a-5p and CDK7 on GA-induced GC progression. Mechanistically, the binding relationship between miR-33a-5p and circ_ASAP2 or CDK7 was predicted with starBase v3.0 online database and verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. In vivo tumor formation assay was used to explain the impacts of GA treatment on GC growth in vivo.
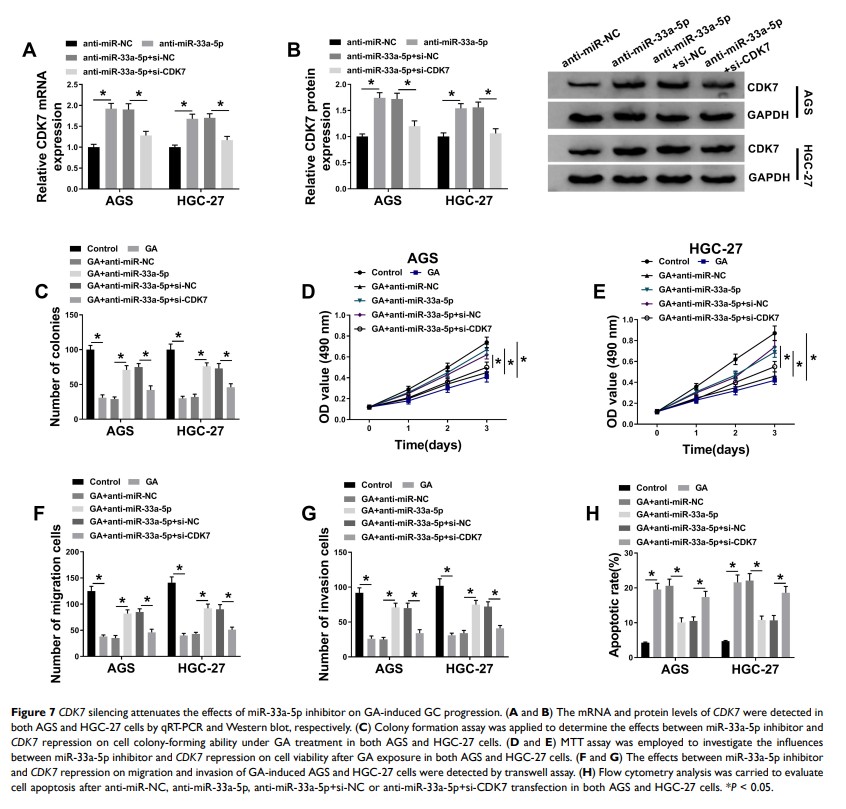
Results: Circ_ASAP2 and CDK7 expression were downregulated in GA-induced GC cells compared with GC cells. MiR-33a-5p expression was upregulated in GA-induced GC cells relative to GC cells. The protein expression level of CDK7 was lower in GA-induced GC cells than that in GC cells. Further, circ_ASAP2 overexpression decreased GA-induced inhibition effects on cell proliferation, migration and invasion and GA-induced promotion effect on cell apoptosis in both AGS and HGC-27 cells, whereas this phenomenon was reversed by miR-33a-5p. In addition, circ_ASAP2 functioned as a sponge of miR-33a-5p and miR-33a-5p was associated with CDK7 . Furthermore, GA treatment inhibited GC growth in vivo.
Conclusion: Circ_ASAP2 overexpression promoted cell proliferation, migration and invasion, whereas inhibited cell apoptosis by upregulating CDK7 expression through binding to miR-33a-5p in GA-induced GC cells. This study provided a theoretical basis in GC treatment with GA.
Keywords: gambogic acid, circ_ASAP2, miR-33a-5p, CDK7, gastric cancer