108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肠道微生物群失调对血脑屏障的影响
Authors Tang W, Zhu H, Feng Y, Guo R, Wan D
Received 20 March 2020
Accepted for publication 30 August 2020
Published 29 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3351—3363
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S254403
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eric Nulens
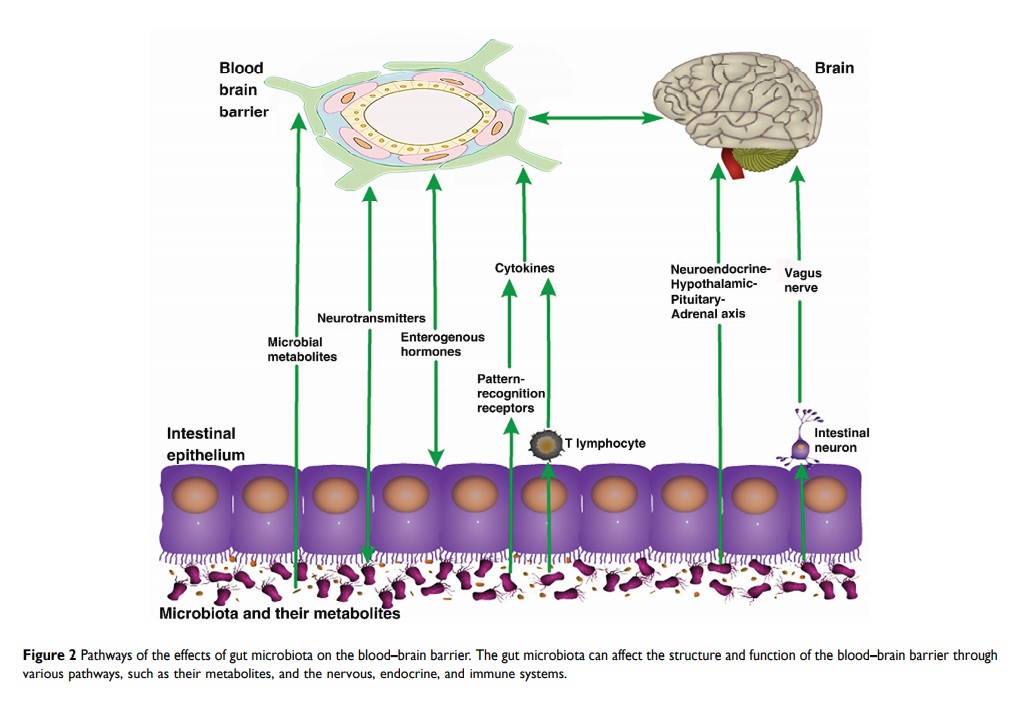
Abstract: The gut microbiota is symbiotic with the human host and has been extensively studied in recent years resulting in increasing awareness of the effects of the gut microbiota on human health. In this review, we summarize the current evidence for the effects of gut microbes on the integrity of the cerebral blood–brain barrier (BBB), focusing on the pathogenic impact of gut microbiota disorders. Based on our description and summarization of the effects of the gut microbiota and its metabolites on the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems and related signaling pathways and the resulting destruction of the BBB, we suggest that regulating and supplementing the intestinal microbiota as well as targeting immune cells and inflammatory mediators are required to protect the BBB.
Keywords: microbiota, metabolites, blood–brain barrier