108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA LINC01106 的沉默可通过调节 miR-449a/MET 轴来遏制子宫内膜癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Gao X, Yu L, Zhang J, Xue P
Received 24 June 2020
Accepted for publication 13 August 2020
Published 29 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9643—9655
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S264642
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
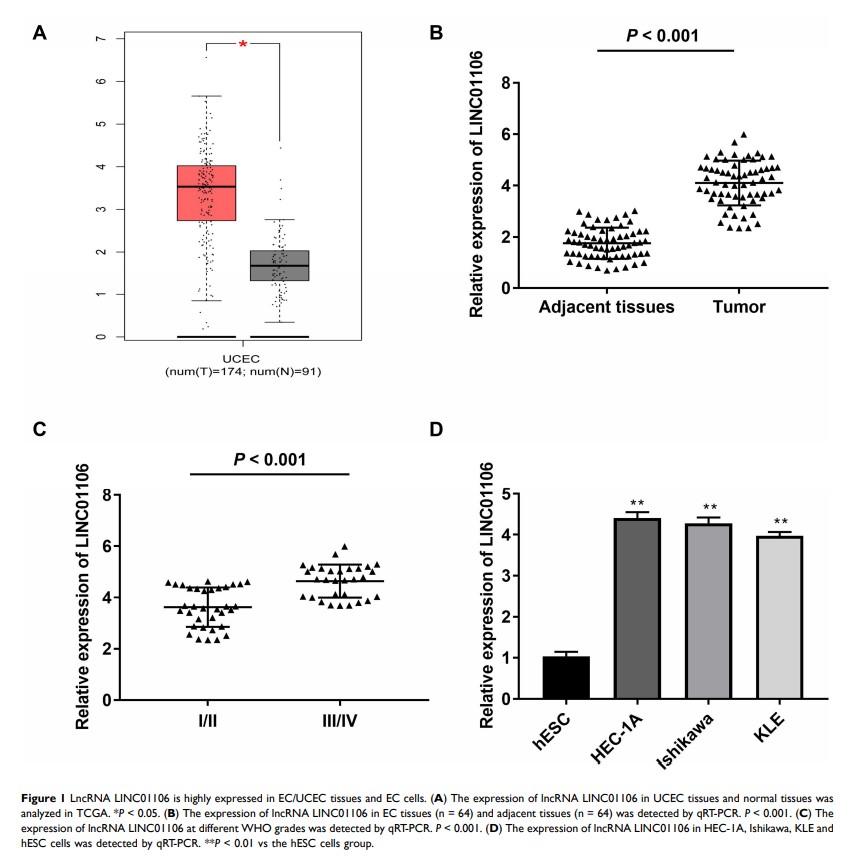
Purpose: Endometrial cancer (EC) is an aggressive tumor in females and the development of EC is considered to regulate by some long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the regulatory mechanism of lncRNA LINC01106 on EC.
Methods: The expression of lncRNA LINC01106, miR-449a and MET in EC tissues and cells was detected by qRT-PCR. Through MTT, wound healing and transwell invasion assays, the proliferation, migration and invasion of EC cells were detected, respectively. The xenograft tumor model was constructed in nude mice to confirm the inhibiting effect of LINC01106 knockdown on EC in vivo. The interactions between miR-449a and LINC01106/MET were predicted by Starbase/Targetscan software and verified by the dual-luciferase reporter assay or RNA immunoprecipitation assay. Western blot assay was performed to determine the protein level of MET.
Results: LncRNA LINC01106 expression was highly up-regulated in EC tissues and cells. The proliferation, migration and invasion of EC cells in vitro were inhibited by the transfection of sh-LINC01106. The growth of tumor xenograft was suppressed by injection of sh-LINC01106. MiR-449a was a target of LINC01106and was negatively modulated by LINC01106. MiR-449a overexpression suppressed the proliferation, migration and invasion of EC cells. In addition, MET was identified as a target gene of miR-449a. Both the high expression of miR-449a and low expression of MET reversed the inhibiting effects of LINC01106 knockdown on Ishikawa cells.
Conclusion: Silencing of LINC01106 inhibits the occurrence and development of EC via regulating the miR-449a/MET axis. This study provides a possible therapeutic strategy for EC.
Keywords: endometrial cancer, lncRNA LINC01106, miR-449a, MET