108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

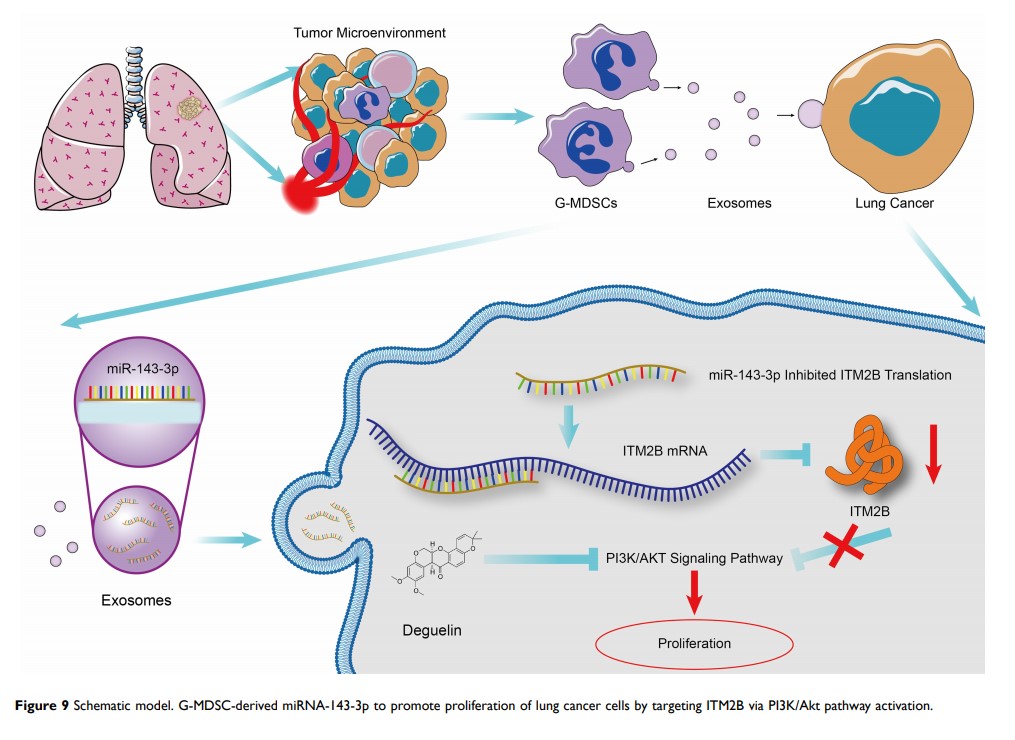
G-MDSCs 衍生的外泌体 miRNA-143-3p 通过靶向 ITM2B 促进肺癌的增殖
Authors Zhou J, Yao Z, Zheng Z, Yang J, Wang R, Fu S, Pan X, Liu Z, Wu K
Received 15 April 2020
Accepted for publication 19 August 2020
Published 30 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9701—9719
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S256378
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Background: The immune environment of lung cancer is complex, and the critical immune factors that promote lung cancer progression need to be explored. Granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSCs) are regarded as immune suppressing cells. However, they also promote tumor progression through other ways, which needs to be explored further. Therefore, we sought to study the regulatory mechanisms underlying the cancer promoting function of G-MDSCs in lung cancer.
Methods: G-MDSCs were isolated from lung cancer tissues using flow cytometry. Exosomes were separated from the G-MDSCs supernatant by ultracentrifugation and verified using flow cytometry, Western blot, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). RNA sequencing was used to identify the differential miRNAs and genes. Real-time quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) confirmed these results. The proliferation rate was assessed using the CCK-8 assay. Lentiviral vectors were used to alter the expression of the miRNAs and genes to analyze their effects on lung cancer progression.
Results: G-MDSCs secreted more exosomes in the lung cancer tissues, which promoted cancer progression by accelerating proliferation. Micro RNA-143-3p (miR-143-3p) increased in G-MDSCs derived exosomes and downregulated integral membrane protein 2B (ITM2B ) by targeting the 3ʹ-untranslated region (UTR) region. Overexpression of miR-143-3p enhanced proliferation by inhibiting transcription of ITM2B to activate the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which can be blocked by deguelin. This phenomenon was further confirmed by accelerated tumor growth and worse prognosis in mice.
Conclusion: The key findings of this study highlight the potential of the G-MDSC-derived exosomes and the miR-143-3p/ITM2B axis as therapeutic targets and clinical indicators of lung cancer.
Keywords: G-MDSCs, exosomes, miRNA-143-3p, ITM2B, proliferation, lung cancer