108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA H19 通过激活自噬参与牙周组织炎症
Authors Guo R, Huang Y, Liu H, Zheng Y, Jia L, Li W
Received 11 August 2020
Accepted for publication 12 September 2020
Published 30 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 635—646
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S276619
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ning Quan
Purpose: Periodontitis is the leading cause of tooth loss. The role of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in periodontal inflammation remains unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of lncRNA H19 in periodontitis and its possible regulation of autophagy in periodontitis.
Material and Methods: Inflammation level was determined by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in periodontal ligament cells (PDLCs). Western blotting, flow cytometric analysis, and immunofluorescence staining were used to detect the autophagy flux. Overexpression or knockdown of H19 was used to confirm its function. Ligature-induced periodontitis model in mice and periodontitis-affected human gingival tissue were used in vivo. RNA sequencing was performed to determine the differentially expressed genes.
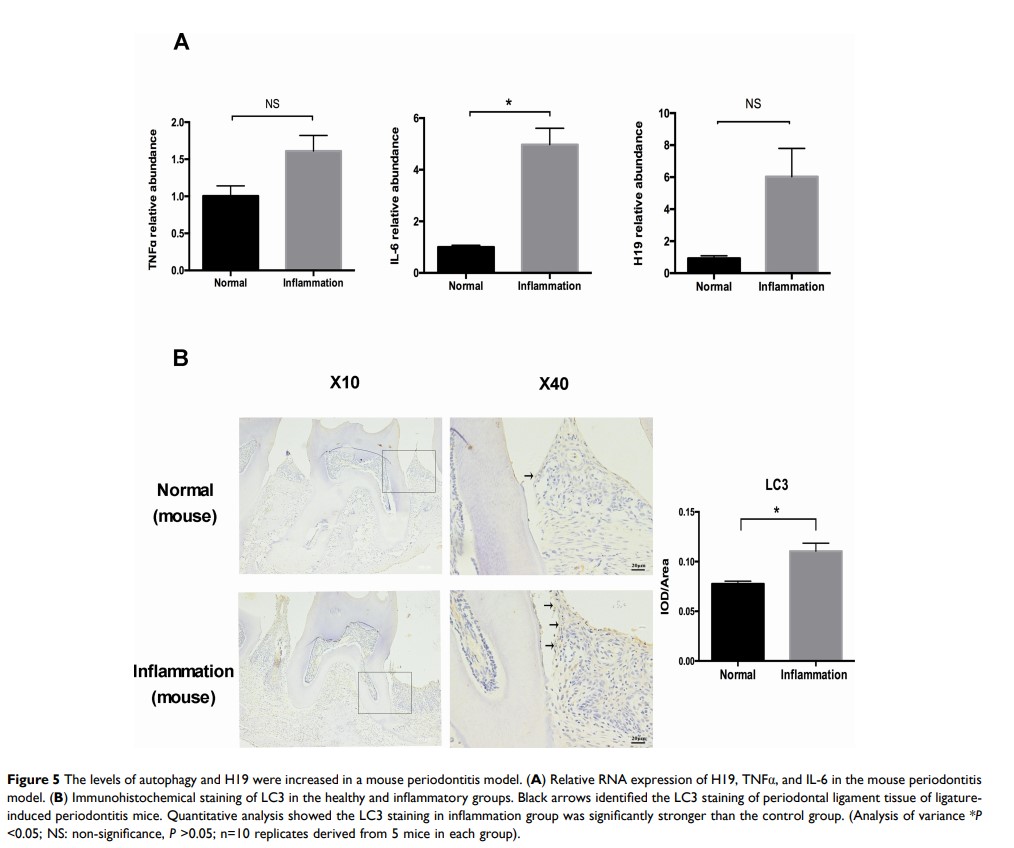
Results: Autophagy was significantly increased in PDLCs after inflammatory stimulation as well as in a ligature-induced periodontitis model in mice and periodontitis-affected human gingival tissue. During the inflammatory process, H19 expression was also significantly upregulated. Further, the levels of autophagic markers were significantly upregulated after overexpressing H19 in PDLCs, and the increased autophagic activity induced by inflammatory stimulation was reversed by H19 knockdown. RNA sequencing showed that the expression profiles of mRNAs were significantly altered after H19 overexpression, and the differentially expressed genes were enriched in the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which was confirmed by the decreased p-AKT protein expression in the H19 overexpression group.
Conclusion: Periodontal inflammation activates autophagy flux, and H19 mediates the activation of autophagy via AKT pathway in periodontitis. This study expands our understanding of molecular regulation in periodontitis.
Keywords: autophagy, periodontitis, long non-coding RNA