108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

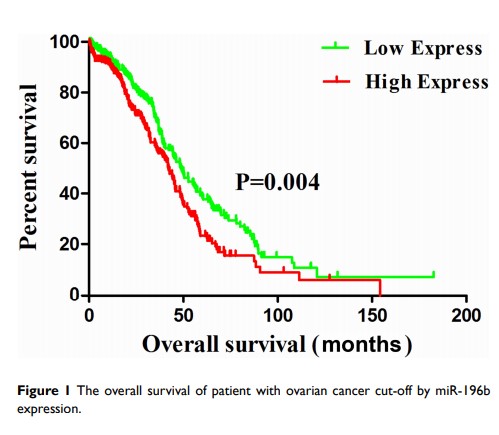
miR-196b 的高表达预测卵巢癌患者的预后不良
Authors Li Y, Li J, Liu Z, Zhang Y
Received 27 March 2020
Accepted for publication 20 August 2020
Published 1 October 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9797—9806
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S254942
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background/Aims: To analyze the clinical significance of miR-196b expression in ovarian cancer and predict the function and possible mechanism of miR-196b.
Methods: Both Kaplan–Meier (K-M) and Cox proportional hazards regression model were used to analyze the prognostic factors of patients with ovarian cancer. MiR196-b was modulated in ovarian cancer cells, and the cell viability, cell cycle, and cell cycle-related gene expression were analyzed. The target genes of miR-196b were then predicted and checked the relationship between the target genes.
Results: MiR-196b was an independent risk factor, while high expression of miR-196b was associated with poor prognosis of ovarian cancer. MiR-196b overexpression increased cancer cell proliferation. Cdkn1b, as one of the targets of miR-196b, was related to cell viability and mitosis.
Conclusion: High expression of miR-196b was significantly associated with poor prognosis of the patients with ovarian cancer. MiR-196b could increase the cell proliferation of ovarian cancer by modulating Cdkn1b expression.
Keywords: microRNAs, MiR-196b, ovarian cancer, Cdkn1b, proliferation