108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

高风险非肌肉浸润性膀胱癌患者术前预后营养指数和全身免疫炎症指数对长期生存的预测价值:单中心回顾性研究
Authors Bi H, Shang Z, Jia C, Wu J, Cui B, Wang Q, Ou T
Received 21 April 2020
Accepted for publication 26 August 2020
Published 1 October 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9471—9483
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S259117
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the associations between the preoperative prognostic nutritional index (PNI), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) in high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) patients who received intravesical instillation of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) after transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT).
Patients and Methods: We retrospectively collected data from 387 high-risk NMIBC patients between January 2004 and December 2014. PNI was calculated as total lymphocyte count (109/L)× 5+albumin concentration (g/L). SII was calculated as neutrophil count (109/L)×platelet count (109/L)/lymphocyte count (109/L). The cutoff values of PNI and SII were determined through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. OS and CSS were estimated by Kaplan–Meier analysis. The Log rank test was used to compare differences between the groups. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed to assess the predictive values of PNI and SII for OS and CSS. Additionally, highest-risk NMIBC patients were also divided into low or high groups according to PNI and SII. The OS and CSS of highest-risk NMIBC patients were estimated using Kaplan-Meier analysis with the Log rank test.
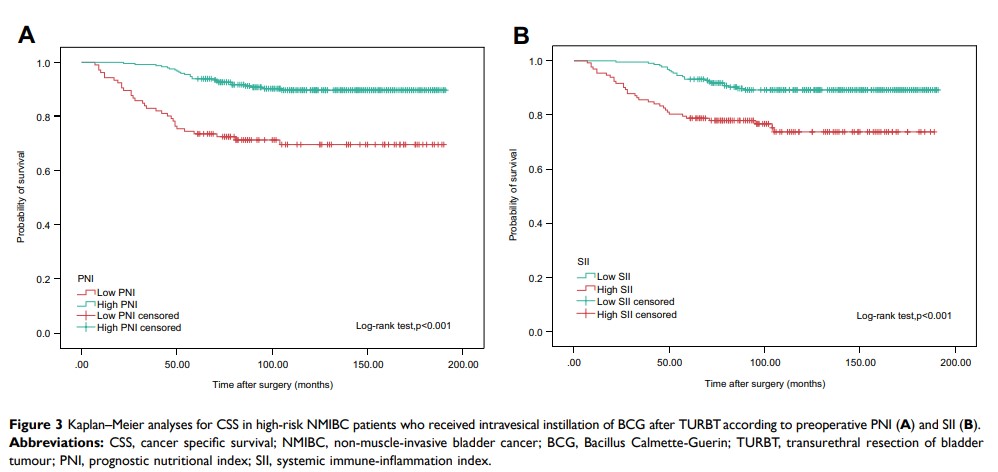
Results: The patients were divided into two groups according to the cutoff values of PNI (< 50.17 vs ≥ 50.17) and SII (< 467.76 vs ≥ 467.76). Kaplan–Meier analysis revealed that low PNI and high SII were associated with poorer OS and CSS in high-risk NMIBC patients. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses revealed that PNI and SII were independent predictive factors for OS and CSS. Kaplan–Meier analysis also revealed that low PNI and high SII were related to poorer OS and CSS in highest-risk NMIBC patients.
Conclusion: These results suggest that preoperative PNI and SII, based on standard laboratory measurements, may be useful noninvasive, inexpensive and simple tools for predicting the long-term survival of high-risk NMIBC patients who received intravesical instillation of BCG after TURBT.
Keywords: prognostic nutritional index, systemic immune-inflammation index, non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, Bacillus Calmette-Guerin, overall survival, cancer-specific survival