108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

姜黄素通过调节 miR-200c/EPM5 改变大肠癌上皮-间质转化
Authors Wang H, Cai X, Ma L
Received 4 May 2020
Accepted for publication 21 August 2020
Published 1 October 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9405—9415
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S260129
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: The serious side effect of current conventional treatments for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) highlights the requirement of an alternative treatment strategy. Natural compounds, such as curcumin, have been gained much attention due to its low toxicity and anti-tumor effect.
Methods: qPCR and Western blot were used to measure the molecular changes induced by curcumin. Wound-healing assay and transwell assay were conducted to study the effect on cell migration and invasion. RT1 PCR array was performed to identify the miRNAs involved in curcumin-repressed EMT. Three algorithms and luciferase reporter assay were used to identify EPM5 as a target of miR-200c. The bioinformatical analysis of TCGA-COAD and other CRC cohorts were used to examine the association of EPM5 with EMT signatures and clinical relevance. The ectopic expression or siRNA-mediated knockdown of EPM5 was applied to study the role of EPM5 in CRC.
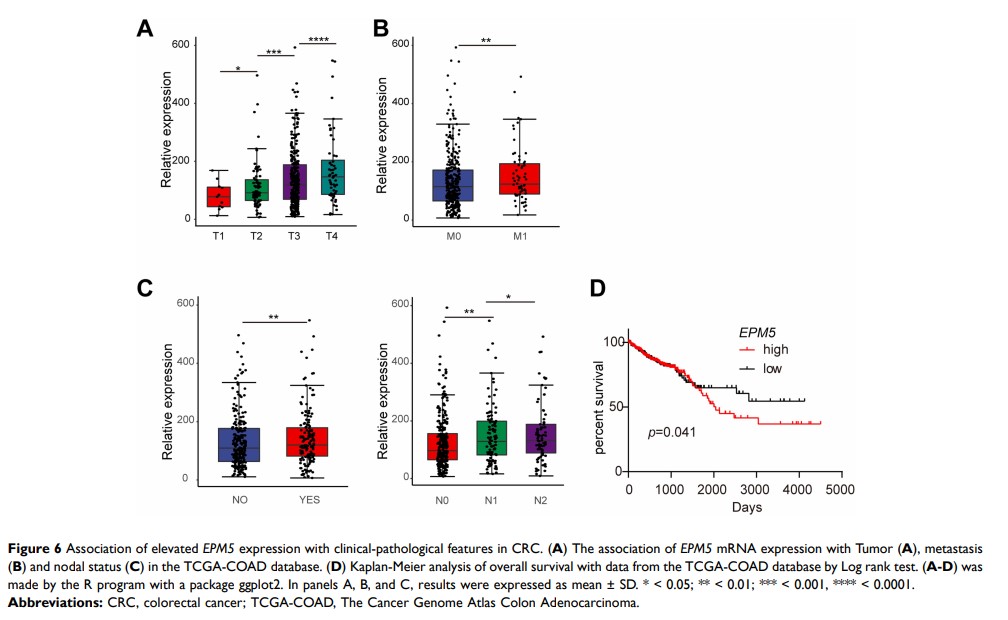
Results: Treatment with curcumin changed the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related gene expression, repressed cell migration and invasion in CRC cells. Its anti-tumor capability required the upregulation of miR-200c. EPM5 was a direct target of miR-200c and enriched in the consensus molecular subtype (CMS) 4 of CRC. Ectopic expression of EPM5 alone was sufficient to induce EMT in CRC. Downregulation of EPM5 was necessary for curcumin-repressed EMT, migration, and invasion. Higher expression of EPM5 was associated with the advanced TNM stages and poor survival in CRC.
Conclusion: Our data provide the first evidence that the curcumin inhibits EMT in CRC by upregulation of miR-200c and downregulation of EPM5, and the use of curcumin might be able to prevent or delay CRC progression.
Keywords: curcumin, EMT, miR-200c, EPM5, CRC