108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA SNHG14 通过调节 miR-93-5p/ZBTB7A 轴阻碍子宫内膜癌细胞的生存能力、迁移和侵袭
Authors Zhang K, Cai Y, Zhou Q, Sun H, Wei J
Received 8 April 2020
Accepted for publication 5 August 2020
Published 1 October 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9515—9525
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S257419
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: The function of long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 14 (SNHG14) in endometrial carcinoma (EC) has not been thoroughly reported. This research is designed to research the action mechanism of SNHG14 in EC development.
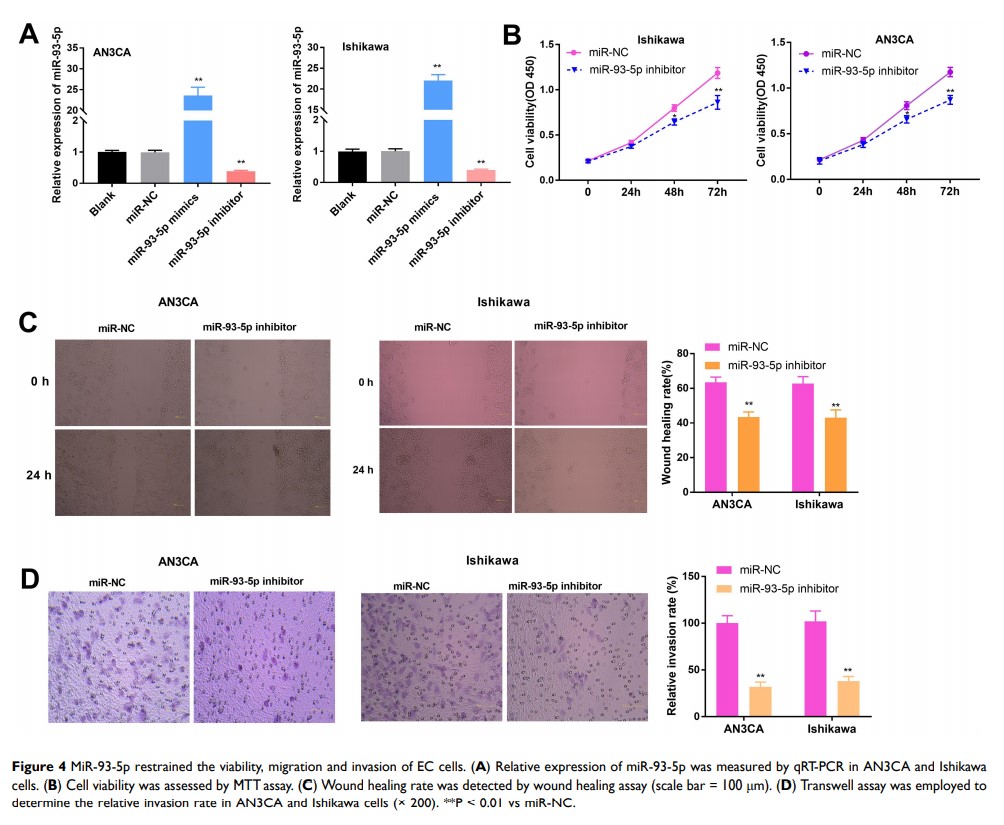
Methods: The expression of SNHG14 was estimated in The Cancer Genome Atlas and was verified by qRT-PCR in EC tissues. The correlation between SNHG14 expression and clinicopathological features of EC patients was analyzed. Cell viability, wound healing rate, and relative invasion rate were examined by MTT, wound healing, and transwell assay. StarBase, TargetScan, RNA pull-down, and dual luciferase reporter gene (DLR) assay were conducted to analyze the relationship among SNHG14, miR-93-5p and ZBTB7A .
Results: SNHG14 was underexpressed in EC. SNHG14 expression was significantly relevant to menstruation, FIGO stage, histological grade and lymphatic metastasis of EC patients. SNHG14 overexpression hampered viability, migration and invasion of EC cells. SNHG14 functioned as a sponge for miR-93-5p, and miR-93-5p inhibition restrained cell viability, migration and invasion in EC. In addition, miR-93-5p directly targeted to ZBTB7A , which was underexpressed in EC. The suppressive action of SNHG14 overexpression on the viability, migration and invasion of EC cells was partly rescued by miR-93-5p overexpression or ZBTB7A silencing.
Conclusion: LncRNA SNHG14 hampered the viability, migration and invasion of EC cells via modulating miR-93-5p/ZBTB7A axis.
Keywords: endometrial carcinoma, invasion, SNHG14, migration, miR-93-5p, ZBTB7A