108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

老年人延续使用共享护士意愿的影响因素实证研究
Authors Xie C, Jia S, He C
Received 23 June 2020
Accepted for publication 4 September 2020
Published 1 October 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1849—1860
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S261827
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
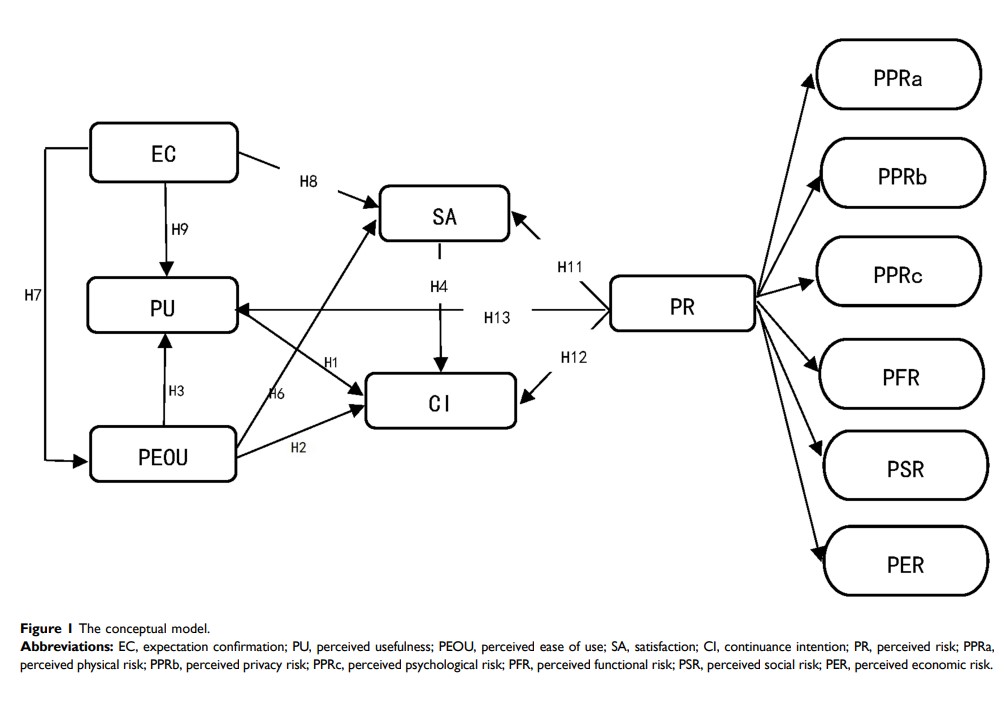
Objective: Based on the technical acceptance model, expectation confirmation model, and perceived risk theory, this study aims to analyze the factors and their effects on shared nurse users’ continuance intention in the process of e-health consumption.
Methods: This research established a measurement tool that fits the topic of this study and a model of shared nurse continuance. From January to May 2020, 373 valid samples from elderly individuals living in urban areas of Jiangxi Province, China, were collected by convenience sampling in order to analyze through empirical research their continuance intentions of selecting shared nurses. The theoretical models and research hypotheses were verified by structural equation modeling with AMOS 25 software.
Results: The measurement model indicated that the theoretical constructs have adequate reliability and validity, while the structured equation model is illustrated as having a high model fit for empirical data. The hypothesis test results showed that expectation confirmation positively affects perceived ease of use; both of them have positive effects on perceived usefulness and satisfaction. Perceived usefulness and satisfaction play an intermediary role in expectation confirmation and continuance intention. Perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness positively affect continuance intention. Perceived risk negatively affects perceived usefulness and continuance intention.
Conclusion: This study expanded the application of the technology acceptance model, expectation confirmation model, and perceived risk model in e-health by investigating the factors that influence elderly users’ continued intention to use shared nurses. Based on these empirical findings, we derived implications for the design and operation of the shared nurse platform, and suggestions on relevant management departments and incentive structures for using e-health. The results of this study provide important implications for further research and practice of mobile health care.
Keywords: e-health, home care, technology acceptance model, expectation confirmation model, perceived risk