108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肥胖脂肪组织炎症和胰岛素抵抗的表征和治疗
Received 9 July 2020
Accepted for publication 1 September 2020
Published 1 October 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3449—3460
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S271509
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ming-Hui Zou
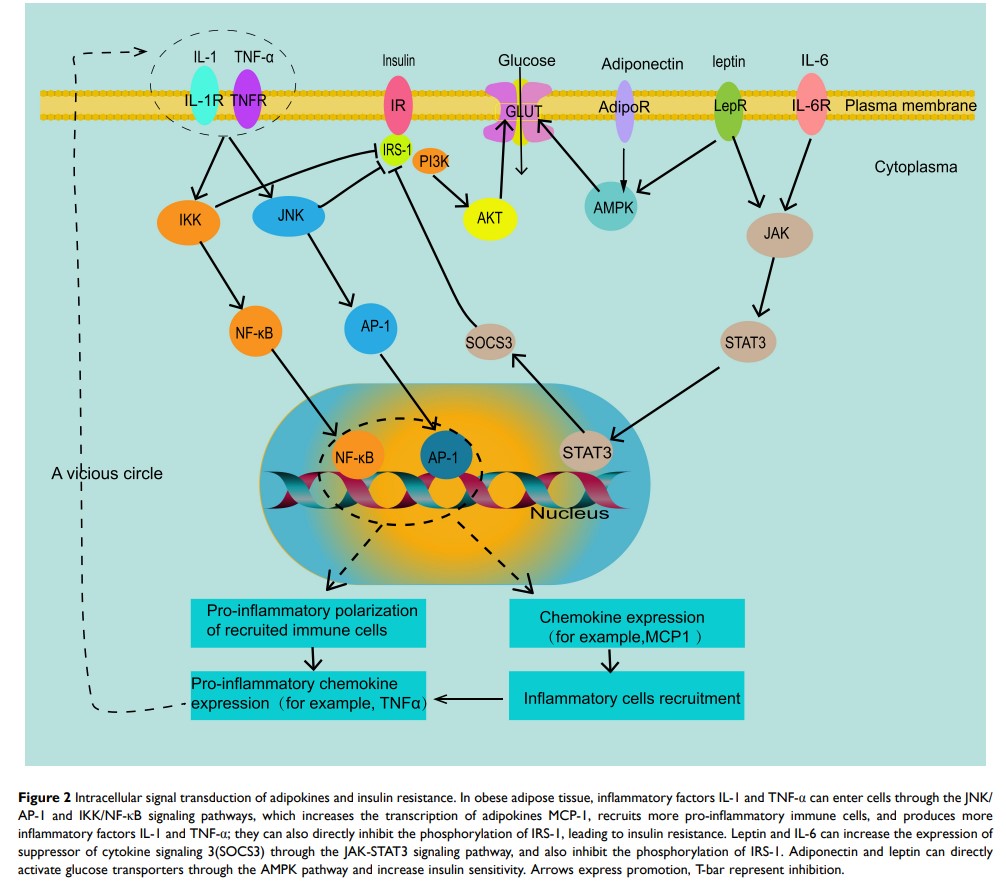
Abstract: Adipose tissue is the largest energy storage and protection organ. It is distributed subcutaneously and around the internal organs. It regulates metabolism by storing and releasing fatty acids and secreting adipokines. Excessive nutritional intake results in adipocyte hypertrophy and proliferation, leading to local hypoxia in adipose tissue and changes in the release of adipokines. These lead to recruit of more immune cells into adipose tissue and release of inflammatory signaling factors. Excess free fatty acids and inflammatory factors interfere with intracellular insulin signaling. In this review, we summarize the characteristics of obese adipose tissue and analyze how its inflammation causes insulin resistance. We further discuss the latest clinical research progress on the control of insulin resistance and inflammation resulting from obesity through anti-inflammatory therapy and bariatric surgery. Our review shows that targeted anti-inflammatory therapy is of great significance for obese patients with insulin resistance.
Keywords: obesity, adipose tissue, inflammation, insulin resistance, anti-inflammatory therapy