108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于全氟化碳的 19F 核磁共振成像在生物医学中的应用
Authors Wu L, Liu F, Liu S, Xu X, Liu Z, Sun X
Received 23 March 2020
Accepted for publication 15 July 2020
Published 2 October 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 7377—7395
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S255084
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
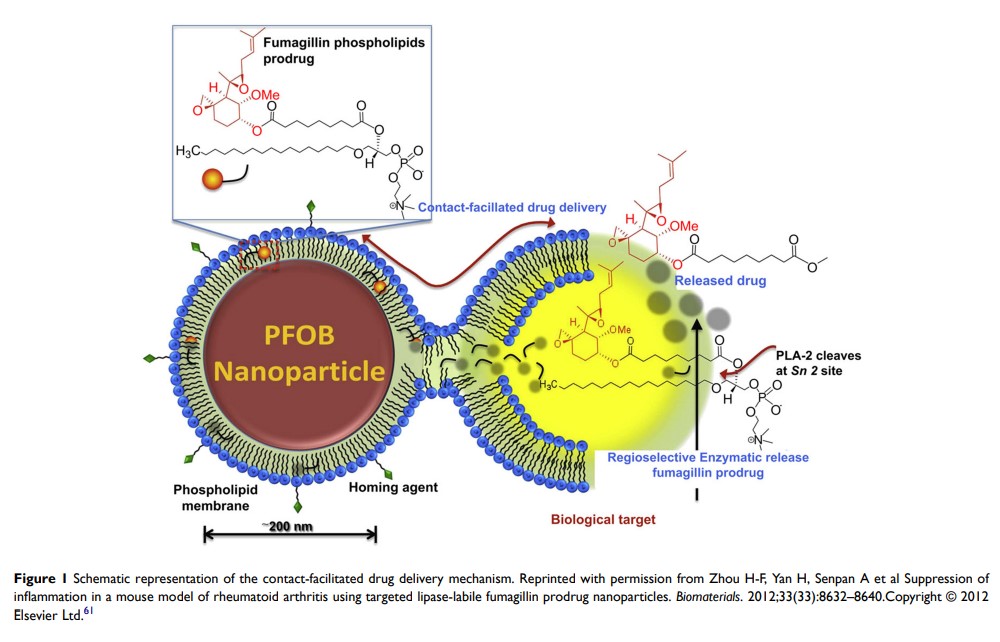
Abstract: Fluorine-19 (19F) magnetic resonance (MR) molecular imaging is a promising noninvasive and quantitative molecular imaging approach with intensive research due to the high sensitivity and low endogenous background signal of the 19F atom in vivo. Perfluorocarbons (PFCs) have been used as blood substitutes since 1970s. More recently, a variety of PFC nanoparticles have been designed for the detection and imaging of physiological and pathological changes. These molecular imaging probes have been developed to label cells, target specific epitopes in tumors, monitor the prognosis and therapy efficacy and quantitate characterization of tumors and changes in tumor microenvironment noninvasively, therefore, significantly improving the prognosis and therapy efficacy. Herein, we discuss the recent development and applications of 19F MR techniques with PFC nanoparticles in biomedicine, with particular emphasis on ligand-targeted and quantitative 19F MR imaging approaches for tumor detection, oxygenation measurement, smart stimulus response and therapy efficacy monitoring, et al.
Keywords: fluorine-19 magnetic resonance imaging, fluorocarbons, nanoparticles, molecular imaging, neoplasms