108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

锌指和 BTB 结构域 4 在结直肠癌中的表达及其临床意义
Authors Xiang T, He K, Wang S, Chen W, Li H
Received 7 June 2020
Accepted for publication 14 September 2020
Published 5 October 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 9621—9626
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S266529
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing 4 (ZBTB4), which is a transcriptional regulator, has been identified as a tumor suppressor in several human carcinomas. So far, however, the expression of ZBTB4 and its possible clinical significance in colorectal cancer (CRC) remain unknown.
Materials and Methods: The mRNA and protein expressions of ZBTB4 in five CRC cell lines were respectively detected by performing qRT-PCR and Western Blotting. ZBTB4 expression in colorectal tissue specimens was determined, and subsequently its relationship with clinical prognosis was examined.
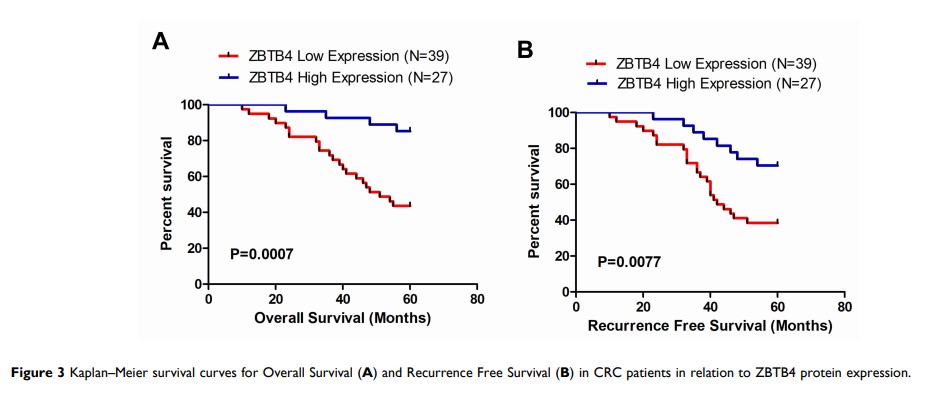
Results: The mRNA and protein expressions of ZBTB4 were significantly decreased in all the five CRC cell lines compared with normal colonic epithelial cells. Consistent with the cell data, immunohistochemical results showed that as compared with the normal colorectal tissue samples, ZBTB4 protein expression was clearly lower in the CRC tissue samples, especially in CRC patients with liver metastasis. In addition, low-expressed ZBTB4 was found associated with tumor metastasis stage (P=0.0003) and level of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) (P=0.0004). The overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in the ZBTB4-low group were significantly lower than those in the ZBTB4-high group (P=0.0007 and P=0.0077).
Conclusion: The current findings showed that patients with high-expressed ZBTB4 in CRC tissues may develop a better prognosis, and ZBTB4 could serve as a potential therapeutic target for CRC treatment.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, ZBTB4 expression, immunohistochemical, clinical significance, prognosis