108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

电针通过 IDO 介导的色氨酸降解途径缓解 LPS 诱导的大鼠抑郁样行为
Authors Zhang K, Liu R, Gao Y, Ma W, Shen W
Received 30 July 2020
Accepted for publication 14 September 2020
Published 5 October 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 2257—2266
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S274778
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
Background: Neuroinflammation is an important pathological mechanism of depression that leads to an increase in indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity and NMDAR activation. This study aimed to observe the effects of electroacupuncture on depression-like behaviour in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated rats and the underlying mechanism.
Methods: Wistar rats were intraperitoneally administered LPS (0.5 mg/kg) for 7 consecutive days to establish a depression model. Electroacupuncture treatment was administered 1 hour after daily LPS injection. The open field test (OFT), forced swimming test (FST), and sucrose preference test (SPT) were used to evaluate the depressive-like behaviours. IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); Trp, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), kynurenine (Kyn) and quinolinic acid (Quin) were detected by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) protein and mRNA were assessed by Western blot and real-time qPCR.
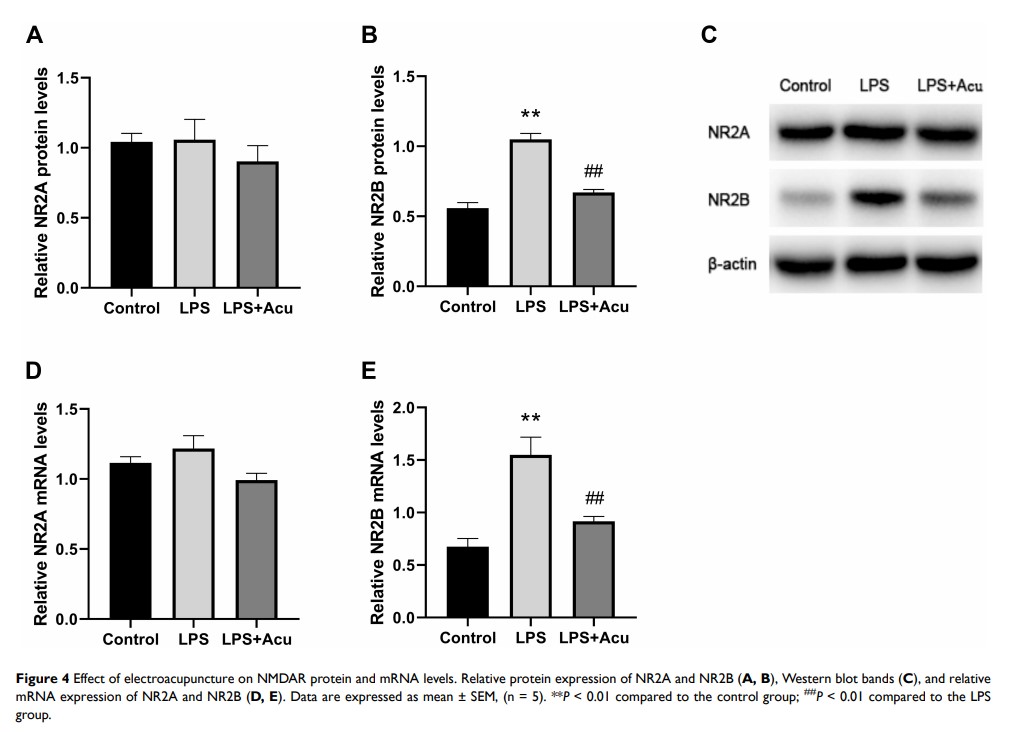
Results: The results showed that electroacupuncture treatment successfully corrected LPS-induced depressive-like behaviour, reduced the inflammatory factor (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) levels in the blood and hippocampus, prevented IDO over-activation and recovered NR2B expression after challenge by LPS.
Conclusion: Electroacupuncture treatment provided protection against LPS-induced depressive-like behaviour, and the associated mechanisms may be related to inhibiting the inflammatory response, regulating the IDO-mediated tryptophan-degrading pathway, and inhibiting NR2B activation.
Keywords: depression, electroacupuncture, LPS, IDO