108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Linc01094 通过海绵化 miR-126-5p 促进胶质母细胞瘤的生长和转移相关特征
Authors Li XX, Yu Q
Received 20 May 2020
Accepted for publication 1 August 2020
Published 6 October 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 9917—9928
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S263091
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
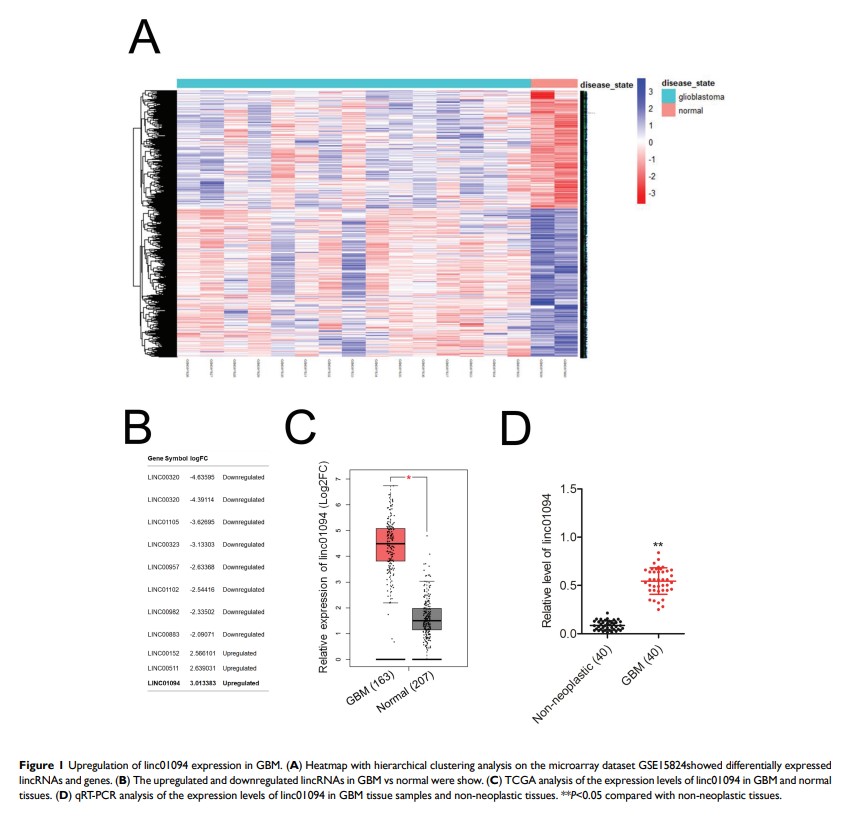
Background: Long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) are associated with the progression of glioblastoma (GBM). However, how linc01094 contributes to the growth and metastatic phenotypes of GBM remains not fully studied.
Methods: The expression levels of linc01094 and miR-126-5p in GBM tissues and cell lines were analyzed using qRT-PCR. Loss-of-function experiments were performed to detect the biological activity of linc01094 in GBM. Glioblastoma tumor model was constructed to explore the impact of linc01094 on GBM cell growth in vivo. Linc01094-sponged miR-126-5p was certified by luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP). The protein expression of miRNA target gene, dynactin subunit 4 (DCTN4) was detected using Western blotting assay.
Results: Herein, we observed that the level of linc01094 was higher in GBM tissues. Silencing of linc01094 restrained the growth and invasive abilities of GBM cell. Moreover, linc01094 level was negatively associated with miR-126-5p level in GBM and linc01094 acted as a “sponge” for miR-126-5p. Reintroduction of linc01094 reversed the tumor-inhibiting effects of miR-126-5p in GBM.
Conclusion: Altogether, linc01094 promoted the tumorigenesis and metastatic phenotypes of GBM cell by modulating of miR-1126-5p/DCTN4 signaling axis.
Keywords: linc01094, GBM, miR-126-5p, DCTN4