108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RNF128 通过 EGFR/MEK/ERK 途径促进肝细胞癌的恶性行为
Authors Bai XS, Zhang C, Peng R, Jiang GQ, Jin SJ, Wang Q, Ke AW, Bai DS
Received 6 July 2020
Accepted for publication 28 August 2020
Published 9 October 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 10129—10141
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S269606
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Background: The ubiquitin-proteasome system participates in the pathogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As an E3 ubiquitin ligase, RNF128 has been proved vital in carcinogenesis, whereas, little is known about the oncogenic mechanisms of RNF128 in HCC.
Materials and Methods: Through tissue microarray from HCC patients, we analyzed RNF128 expression and its relationship with clinical outcomes in HCC. Western blot and quantitative realtime polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were performed to examine expression levels of RNF128 in HCC tissues and cell lines. Effects of RNF128 on HCC cellular biological functions and the potential mechanism were evaluated through knockdown and overexpression assays in vitro and in vivo methods.
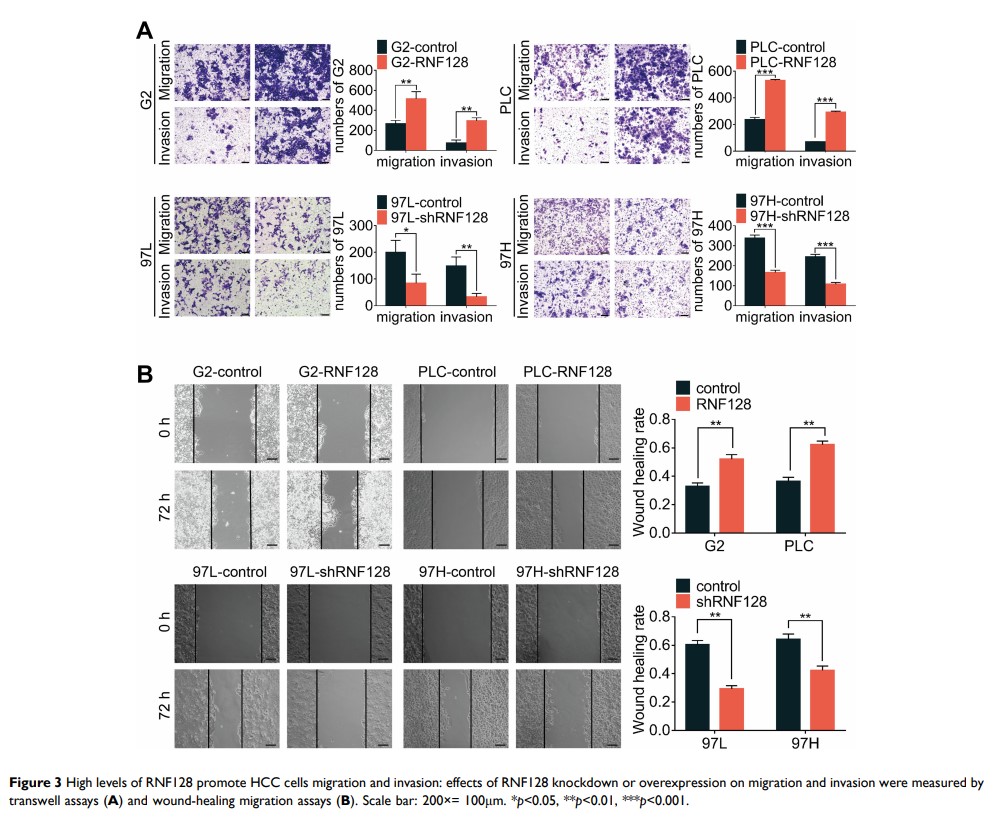
Results: RNF128 expression was found to be remarkably elevated in HCC tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. Furthermore, the overexpression of RNF128 enhanced hepatoma cells proliferation, colony formation, migration, invasion, and apoptotic resistance both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, RNF128 activated EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and the EGFR inhibitor, gefitinib partially reversed RNF128-enhanced proliferation, invasion, and migration in hepatoma cells.
Conclusion: RNF128 promotes HCC progression by activating EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway, which might function as a novel prognostic molecular signature with the potential to be a candidate therapeutic target for HCC patients.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, RNF128, ubiquitination, EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway, prognosis