111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA (linc-UBC1) 的过表达与不良预后相关,并能促进结肠直肠癌中的细胞增殖、迁移和侵入
Authors Gao X, Wen J, Gao P, Zhang G, Zhang G
Received 3 December 2016
Accepted for publication 31 December 2016
Published 22 February 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1017—1026
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S129343
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Abstract: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) serve comprehensive roles in various
diseases, including cancer. lncRNA upregulated in bladder cancer 1 (linc-UBC1)
is a notable biomarker of prognosis in certain cancer types; however, its
involvement in the progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unknown. The
present study aimed to investigate the expression of linc-UBC1 in patients with
CRC and to investigate its effect on CRC cells. The expression levels of
linc-UBC1 were estimated by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain
reaction in clinical CRC specimens and matched adjacent non-tumor mucosa from
96 cases of CRC, as well as in a number of CRC cell lines. In addition, the
biological roles of linc-UBC1 were examined using a cell counting kit-8 assay,
flow cytometry, and migration and invasion assays following the downregulation
of linc-UBC1 by small interfering RNA. The results revealed that linc-UBC1 was
significantly overexpressed in CRC tissues and the majority of CRC cell lines
compared with the matched non-tumor mucosa and normal intestinal epithelial
cells. Furthermore, high expression levels of linc-UBC1 were significantly
associated with large tumor size, greater tumor depth, lymph node metastasis,
and advanced tumor-node-metastasis stages. Patients with abnormal expression of
linc-UBC1 had poorer overall survival times according to Kaplan–Meier analyses.
Furthermore, multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that linc-UBC1 was
a significant independent prognostic factor. The results also revealed that
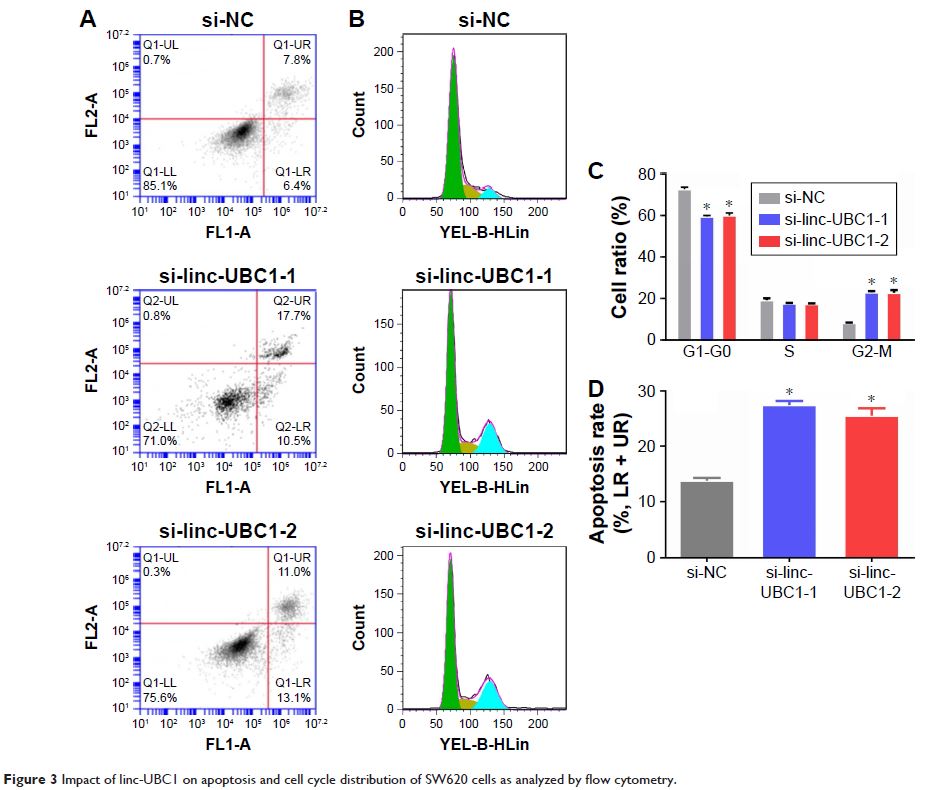
reducing the expression of linc-UBC1 led to the inhibition of migration,
invasion, and proliferation of CRC cells in vitro. Taken together, the results
of the present study suggest that overexpression of linc-UBC1 promotes
proliferation and metastasis in CRC, and may be considered as a novel
diagnostic marker of CRC.
Keywords: linc-UBC1, long non-coding RNA,
colorectal cancer, diagnosis, prognosis, gene function