111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在慢性阻塞性肺疾病 (COPD) 氧化应激过程中的线粒体改变
Authors Jiang Y, Wang X, Hu D
Received 13 December 2016
Accepted for publication 22 March 2017
Published 13 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1153—1162
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S130168
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Charles Downs
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
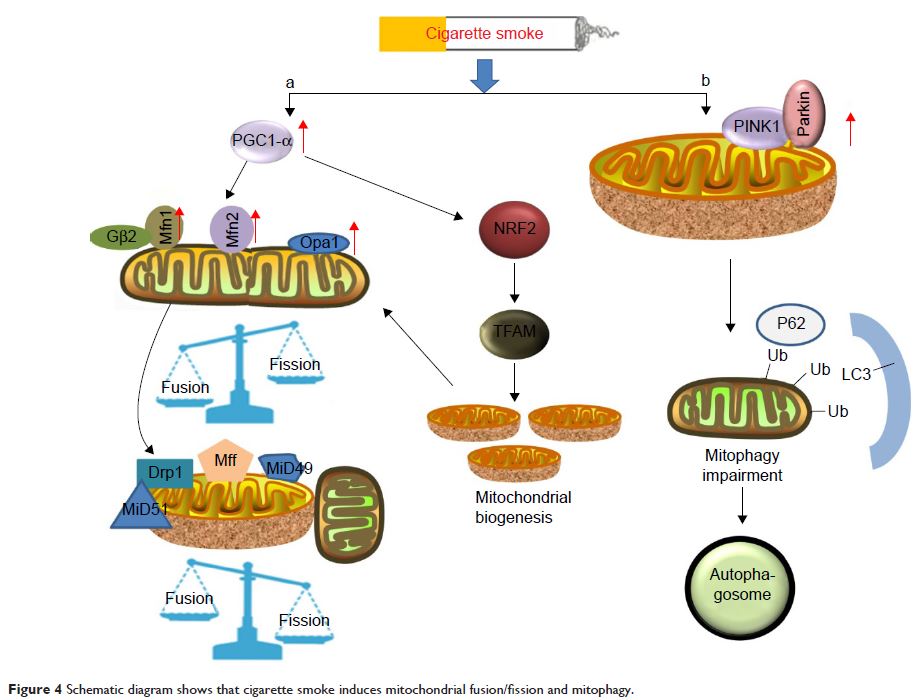
Abstract: The high incidence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), one
of the most prevalent diseases worldwide, has attracted growing attention.
Cigarette smoking is considered a major contributory factor in the pathogenesis
and progression of COPD due to the tremendous oxidative burden that it causes,
which induces an oxidant/antioxidant imbalance. Excessive oxidation induced by
the excessive generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species disturbs the
antioxidant systems and plays an important role in triggering and promoting
chronic inflammation of airways. Given that mitochondria is one of the main
sites of reactive oxygen species production by the oxidative phosphorylation
process, oxidative stress may affect mitochondrial function by changing its
structure and morphology and by affecting a series of mitochondrial proteins.
In particular, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1/Parkin and p62 play critical
roles in mitophagy. During the process, the Akt ubiquitin E3 ligase is an
important mediator associated with cigarette smoke exposure-induced pulmonary
endothelial cell death and dysfunction. Thus, understanding the underlying
mechanisms of the signaling pathway may provide important information regarding
the therapeutic treatment of COPD by application of alternative PTEN-induced
putative kinase 1 targets or ubiquitin E3 ligase.
Keywords: chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease, reactive oxidative stress, reactive nitrogen
stress, mitochondrial fission/fusion, mitophagy