111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

野生型和 24 CYP2D6 等位基因变体的功能特征对吉非替尼 (Gefitinib) 体外代谢的影响
Authors Fang P, Zheng X, He JY, Ge HL, Tang PF, Cai JP, Hu GX
Received 3 February 2017
Accepted for publication 30 March 2017
Published 21 April 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1283—1290
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S133814
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6), a member of the CYP450 enzyme
super family, is a polymorphic enzyme that metabolizes ~25% of therapeutic
drugs. CYP2D6 exhibits significant genetic polymorphisms which might cause
adverse effects and therapeutic failures of some drugs.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the
catalytic activities of 22 novel CYP2D6 alleles (CYP2D6*87 , *88 , *89 , *90 , *91 , *92 , *93 , *94 , *95 , *96 , *97 , *98 , R25Q , F164L , E215K , F219S , V327M , D336N , V342M , R344Q , R440C , R497C ) on the metabolism
of gefitinib in vitro.
Methods and results: CYP2D6 variants were incubated with 1–100 µM gefitinib
for 60 min at 37°C and the reaction was terminated by cooling to -80°C
immediately. Gefitinib and its metabolite O -desmethyl gefitinib were
analyzed by an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
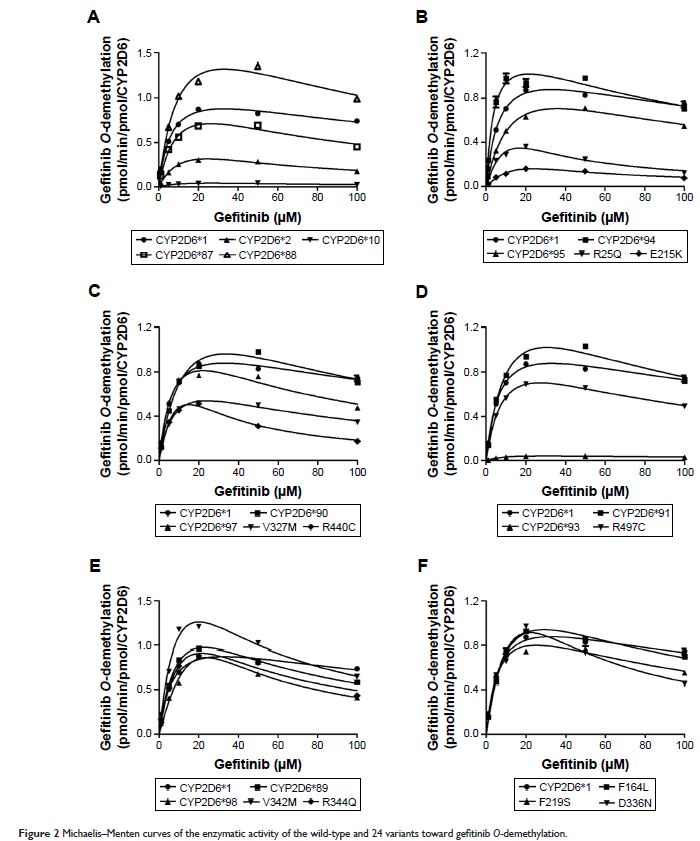
system. Compared to CYP2D6.1, most CYP2D6 variants exhibited significantly
decreased relative clearance values (from 3.11% to 79.35%), whereas CYP2D6.92 and
CYP2D6.96 displayed no detectable enzyme activity. Only CYP2D6.94 exhibited a
markedly increased intrinsic clearance value, and eight variants (CYP2D6.88,
CYP2D6.89, CYP2D6.91, CYP2D6.97, V342M, R344Q, F219S, and F164L) showed no
significant difference. In addition, 23 CYP2D6 allelic isoforms exhibited
substrate inhibition trend toward gefitinib.
Conclusion: As the first study of all the aforementioned alleles
for gefitinib metabolism, these comprehensive data may help in the clinical
assessment of the metabolism of gefitinib, and may also offer a reference for
personalized treatment with gefitinib in clinical settings.
Keywords: CYP2D6, genetic polymorphism, drug
metabolism, gefitinib, enzymatic activity, personalized treatment, NSCLC