111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

EGFR T790M 新发和获得性突变对接受 EGFR-TKIs 治疗的非小细胞肺癌 (NSCLC) 患者的预后影响的综合分析
Authors Liu Y, Sun L, Xiong Z, Sun X, Zhang S, Ma J, Han C
Received 24 January 2017
Accepted for publication 25 March 2017
Published 24 April 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2267—2279
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S133082
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Purpose: The purpose of this meta-analysis was to explore the influences of
pretreatment de novo and posttreatment-acquired epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGFR ) T790M mutations in patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who had received tyrosine
kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and the China National Knowledge
Infrastructure database for eligible literature. Data were extracted to assess
the hazard ratios (HRs) for progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival
(OS), and post-progression survival (PPS) and the relative ratios (RRs) for
objective response rate (ORR).
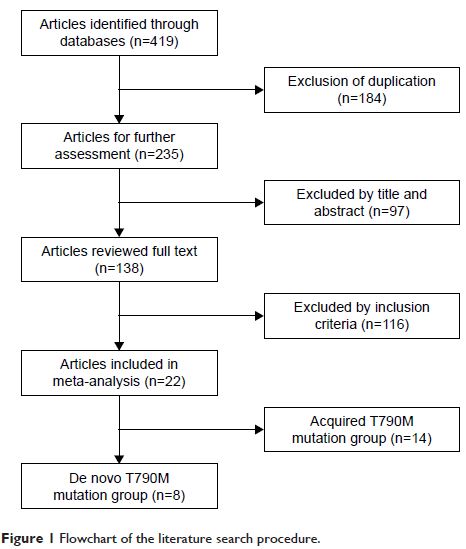
Results: This meta-analysis included 22 studies comprising 1,462 patients with
NSCLC who harbored activating EGFR mutations and were treated with
EGFR-TKIs. Compared to pretreatment T790M mutation-negative NSCLC, pretreatment
T790M mutation-positive NSCLC was associated with decreased PFS (HR 2.23, P <0.001) and OS
(HR 1.55, P =0.003). A trend toward
significance of worsening ORR (RR 0.86, P =0.051) was evident. The acquired
T790M mutation was correlated with improved PFS (HR 0.75, P =0.006) and PPS
(HR 0.57, P <0.001), compared to patients
without the T790M mutation who progressed after EGFR-TKI treatment. There were
no significant differences in OS or ORR between patients with acquired T790M
mutation-positive and T790M mutation-negative NSCLC. However, in the tumor
tissue rebiopsy subgroup, patients with acquired T790M mutation had improved OS
(HR 0.60, P <0.001) compared to T790M
mutation-negative patients. In the plasma ctDNA subgroup, acquired T790M
mutation decreased the OS (HR 1.87, P <0.001).
Conclusion: Pretreatment T790M mutation was associated with worse PFS and OS in
patients with advanced NSCLC treated with EGFR-TKIs, while acquired T790M
mutation was associated with longer PFS and PPS than T790M mutation-negative
NSCLC. The effects on OS were different between acquired T790M mutation
detected from rebiopsy of tumor tissue and that detected from plasma ctDNA.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, T790M, non-small cell lung cancer,
pretreatment, mutation