111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Mn2+- 协同 PDA @ DOX / PLGA 纳米粒子作为化学-光热肿瘤协同治疗的智能治疗剂
Authors Xi J, Da L, Yang C, Chen R, Gao L, Fan L, Han J
Received 12 January 2017
Accepted for publication 3 April 2017
Published 24 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3331—3345
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S132270
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
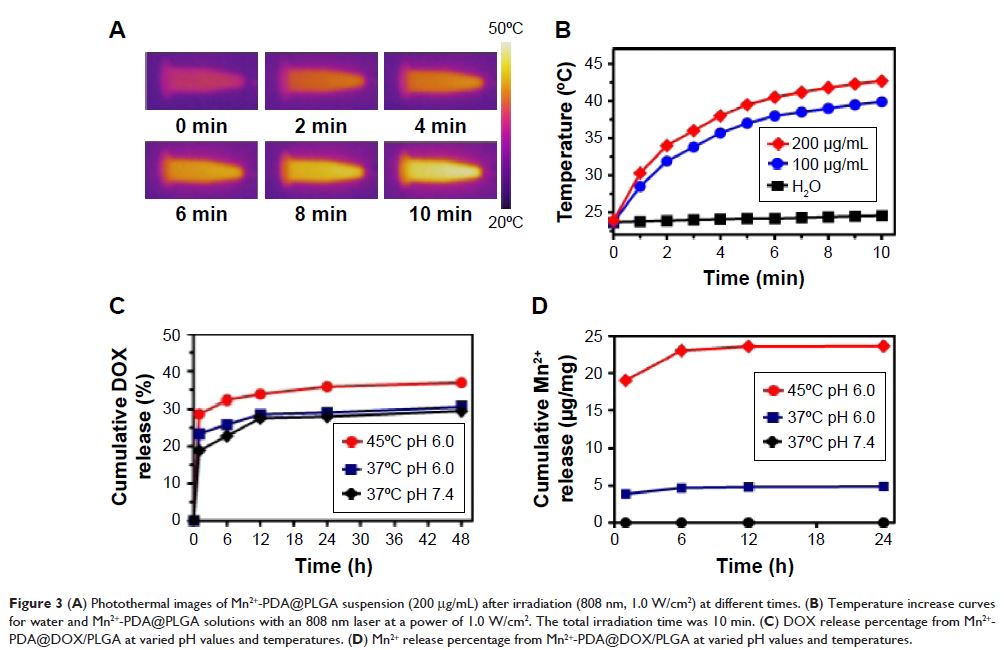
Abstract: Nanoparticle drug delivery carriers, which can implement high
performances of multi-functions, are of great interest, especially for
improving cancer therapy. Herein, we reported a new approach to construct Mn2+-coordinated doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded poly(lactic-co -glycolic acid) (PLGA)
nanoparticles as a platform for synergistic chemo-photothermal tumor therapy.
DOX-loaded PLGA (DOX/PLGA) nanoparticles were first synthesized through a
double emulsion-solvent evaporation method, and then modified with polydopamine
(PDA) through self-polymerization of dopamine, leading to the formation of
PDA@DOX/PLGA nanoparticles. Mn2+ ions were then coordinated on the
surfaces of PDA@DOX/PLGA to obtain Mn2+-PDA@DOX/PLGA
nanoparticles. In our system, Mn2+-PDA@DOX/PLGA
nanoparticles could destroy tumors in a mouse model directly, by thermal energy
deposition, and could also simulate the chemotherapy by thermal-responsive
delivery of DOX to enhance tumor therapy. Furthermore, the coordination of Mn2+ could
afford the high magnetic resonance (MR) imaging capability with sensitivity to
temperature and pH. The results demonstrated that Mn2+-PDA@DOX/PLGA nanoparticles had a great potential
as a smart theranostic agent due to their imaging and tumor-growth-inhibition
properties.
Keywords: PLGA nanoparticles, polydopamine,
chemo-photothermal therapy, smart theranostic agent