110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于量子点磁珠法化验的血液分型定量和多路检测
Authors Xu T, Zhang Q, Fan YH, Li RQ, Lu H, Zhao SM, Jiang TL
Received 25 January 2017
Accepted for publication 23 March 2017
Published 26 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3347—3356
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S133247
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Accurate and reliable blood grouping is essential for safe blood
transfusion. However, conventional methods are qualitative and use only
single-antigen detection. We overcame these limitations by developing a simple,
quantitative, and multiplexed detection method for blood grouping using quantum
dots (QDs) and magnetic beads.
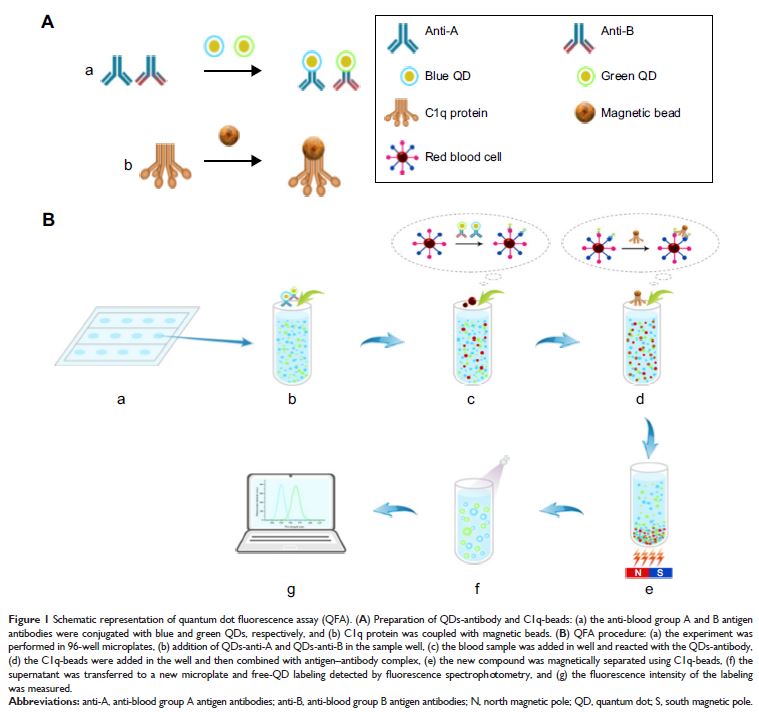
Methods: In the QD fluorescence assay (QFA), blood group A and
B antigens were quantified using QD labeling and magnetic beads, and the blood
groups were identified according to the R value (the value was calculated with
the fluorescence intensity from dual QD labeling) of A and B antigens. The
optimized performance of QFA was established by blood typing 791 clinical
samples.
Results: Quantitative and multiplexed detection for blood group
antigens can be completed within 35 min with more than 105 red
blood cells. When conditions are optimized, the assay performance is
satisfactory for weak samples. The coefficients of variation between and within
days were less than 10% and the reproducibility was good. The ABO blood groups
of 791 clinical samples were identified by QFA, and the accuracy obtained was
100% compared with the tube test. Receiver-operating characteristic curves revealed
that the QFA has high sensitivity and specificity toward clinical samples, and
the cutoff points of the R value of A and B antigens were 1.483
and 1.576, respectively.
Conclusion: In this study, we reported a novel quantitative and
multiplexed method for the identification of ABO blood groups and presented an
effective alternative for quantitative blood typing. This method can be used as
an effective tool to improve blood typing and further guarantee clinical
transfusion safety.
Keywords: blood typing, quantum
dots, magnetic beads, blood group antigens, fluorescence detection