110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

具有还原和 pH 双重灵敏度的低密度脂蛋白偶联胶束用于以智能化的方式将紫杉醇 (paclitaxel) 和 siRNA 共同递送至乳腺肿瘤
Authors Zhu WJ, Yang SD, Qu CX, Zhu QL, Chen WL, Li F, Yuan ZQ, Liu Y, You BG, Zhang XN
Received 1 November 2016
Accepted for publication 3 March 2017
Published 26 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3375—3393
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S126310
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
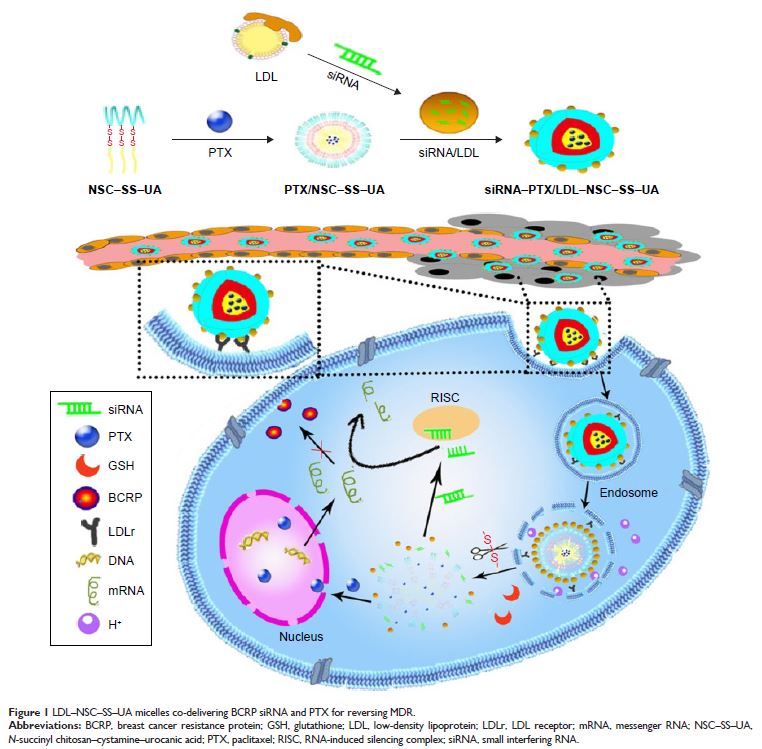
Abstract: Multidrug resistance (MDR) is a major obstacle for the clinical therapy
of malignant human cancers. The discovery of RNA interference provides
efficient gene silencing within tumor cells for reversing MDR. In this study, a
new “binary polymer” low-density lipoprotein–N -succinyl
chitosan–cystamine–urocanic acid (LDL–NSC–SS–UA) with dual pH/redox sensitivity
and targeting effect was synthesized for the co-delivery of breast cancer
resistance protein small interfering RNA (siRNA) and paclitaxel (PTX). In vivo,
the co-delivering micelles can accumulate in tumor tissue via the enhanced
permeability and retention effect and the specific recognition and combination
of LDL and LDL receptor, which is overexpressed on the surface of tumor cell
membranes. The siRNA–PTX-loaded micelles inhibited gene and drug release under
physiological conditions while promoting fast release in an acid
microenvironment or in the presence of glutathione. The micelles escaped from
the lysosome through the proton sponge effect. Additionally, the micelles
exhibited superior antitumor activity and downregulated the protein and mRNA
expression levels of breast cancer resistance protein in MCF-7/Taxol cells. The
biodistribution and antitumor studies proved that the siRNA–PTX-loaded micelles
possessed prolonged circulation time with a remarkable tumor-targeting effect
and effectively inhibited tumor growth. Therefore, the novel dual
pH/redox-sensitive polymers co-delivering siRNA and PTX with excellent
biocompatibility and effective reversal of MDR demonstrate a considerable
potential in cancer therapy.
Keywords: multidrug
resistance, micelle, co-delivery, environmentally sensitive, tumor targeting