110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由金属键 - 配位体配位键驱动的定制刺激响应递送系统
Authors Liang H, Zhou B, He Y, Pei Y, Li B, Li J
Received 21 December 2016
Accepted for publication 23 March 2017
Published 26 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3315—3330
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S130859
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
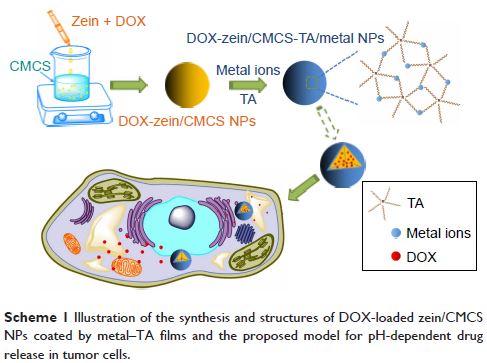
Abstract: In this study, a novel coordination bonding system based on metal–tannic
acid (TA) architecture on zein/carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS) nanoparticles
(NPs) was investigated for the pH-responsive drug delivery. CMCS has been
reported to coat on zein NPs as delivery vehicles for drugs or nutrients in
previous studies. The cleavage of either the “metal–TA” or “NH2–metal” coordination bonds resulted in significant
release of guest molecules with high stimulus sensitivity, especially in mild
acidic conditions. The prepared metal–TA-coated zein/CMCS NPs
(zein/CMCS-TA/metal NPs) could maintain particle size in cell culture medium at
37°C, demonstrating good stability compared with zein/CMCS NPs. In vitro
release behavior of doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX)-loaded metal–TA film-coated
zein/CMCS NPs (DOX-zein/CMCS-TA/metal NPs) showed fine pH responsiveness
tailored by the ratio of zein to CMCS as well as the metal species and feeding
concentrations. The blank zein/CMCS-TA/metal NPs (NPs-TA/metal) were of low
cytotoxicity, while a high cytotoxic activity of DOX-zein/CMCS-TA/metal NPs
(DOX-NPs-TA/metal) against HepG2 cells was demonstrated by in vitro cell assay.
Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and flow cytometry were combined to
study the uptake efficiency of DOX-NPs or DOX-NPs-TA/metal. This system showed
significant potential as a highly versatile and potent platform for drug
delivery.
Keywords: coordination bonding, pH-responsive,
high stimulus sensitivity, drug delivery