110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

上皮 - 间质转化与 NSCLC 细胞中的吉非替尼 (gefitinib) 耐药性相关,同时肝 X 受体配体 GW3965 通过抑制波形蛋白来逆转吉非替尼耐药性
Authors Hu Y, Zang J, Qin X, Yan D, Cao H, Zhou L, Ni J, Yu S, Wu J, Feng JF
Received 15 October 2016
Accepted for publication 11 March 2017
Published 28 April 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2341—2348
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S124757
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Xuqi Li
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Abstract: The role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer drug
resistance is increasingly acknowledged. We examined whether
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition affects gefitinib resistance in non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. Cell viability was detected by CCK-8 assay, VIM expression levels were determined by
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Western blot and immunocytochemistry
were performed to determine the protein expression level of vimentin. We
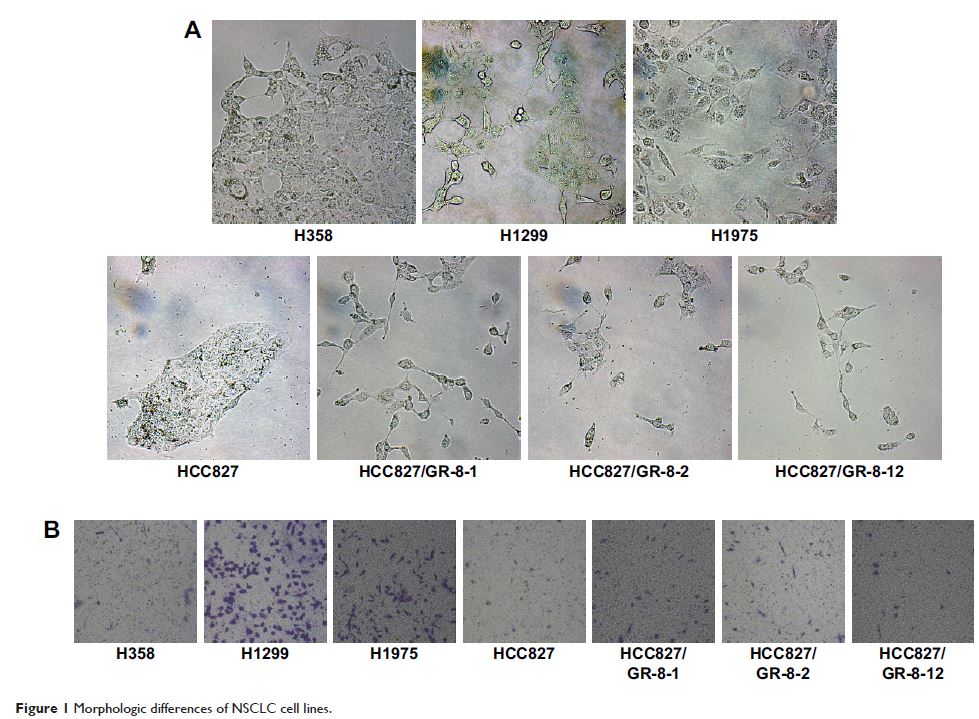
observed morphologic differences between gefitinib-sensitive and -insensitive
cells. Compared with the sensitive parental cell line, HCC827, vimentin
expression levels were increased in HCC827 cells with acquired gefitinib
resistance. Vimentin expression was also markedly upregulated in cells with
intrinsic gefitinib resistance, and upregulated vimentin expression was
correlated with gefitinib sensitivity. Our previous study demonstrated that
coadministration of gefitinib and GW3965 resulted in decreased cell
proliferation and induced apoptosis. Therefore, we investigated the
relationship among GW3965, vimentin, and gefitinib resistance in NSCLC cells by
analysis of the expression of vimentin in cells treated with a combination of
gefitinib and GW3965. Gefitinib treatment led to increased levels of
intracellular vimentin, while combined treatment with gefitinib and GW3965
resulted in decreased vimentin expression levels through reduction of gefitinib
drug resistance in NSCLC cells. Overall, these findings suggest that vimentin
expression is associated with sensitivity to gefitinib, and our study
highlights the potential usefulness of the drug, GW3965, for reversal of gefitinib
resistance through inhibition of vimentin expression.
Keywords: gefitinib resistance, LXR, EMT,
GW3965, vimentin