110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用超临界 CO2 流体强制分散溶液技术制备玉米蛋白纳米粒子,并通过计算流体动力学予以阐明 CO2
Authors Li S, Zhao Y
Received 21 February 2017
Accepted for publication 3 April 2017
Published 2 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3485—3494
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S135239
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Nanoparticles have attracted more and more attention in the medicinal
field. Zein is a biomacromolecule and can be used as a carrier for
delivering active ingredients to prepare controlled release drugs. In this
article, we presented the preparation of zein nanoparticles by
solution-enhanced dispersion by supercritical CO2 (SEDS) approach. Scanning electron
microscopy and transmission electron microscopy were applied to characterize
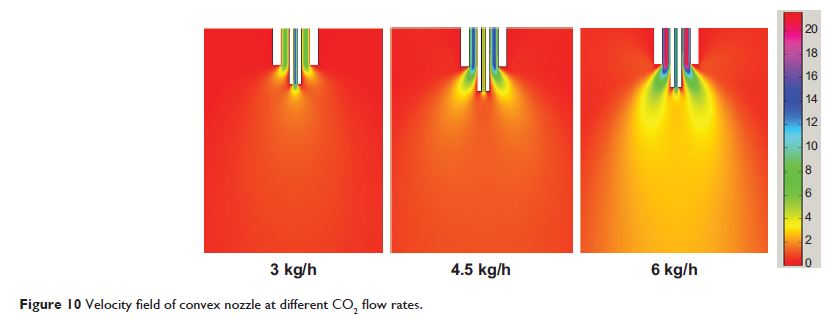
the size and morphology of the obtained particles. The nozzle structure and the
CO2 flow
rate greatly affected the morphology and the size of the particles. The size of
zein was able to be reduced to 50–350 nm according to the different
conditions. The morphologies of the resultant zein were either sphere or the
filament network consisted of nanoparticles. The influence of the nozzle
structure and the CO2 flow rate on the velocity field was
elucidated by using computational fluid dynamics. The nozzle structure and the
CO2 flow
rate greatly affected the distribution of the velocity field. However, a
similar velocity field could also be obtained when the nozzle structure or the
CO2 flow
rate, or both were different. Therefore, the influence of the nozzle structure
and the CO2 flow
rate on the size and morphology of the particles, can boil down to the velocity
field. The results demonstrated that the velocity field can be a potential
criterion for producing nanoparticles with controllable morphology and size,
which is useful to scale-up the SEDS process.
Keywords: nozzle structure, supercritical
antisolvent, zein nanoparticles, computational fluid dynamics