110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

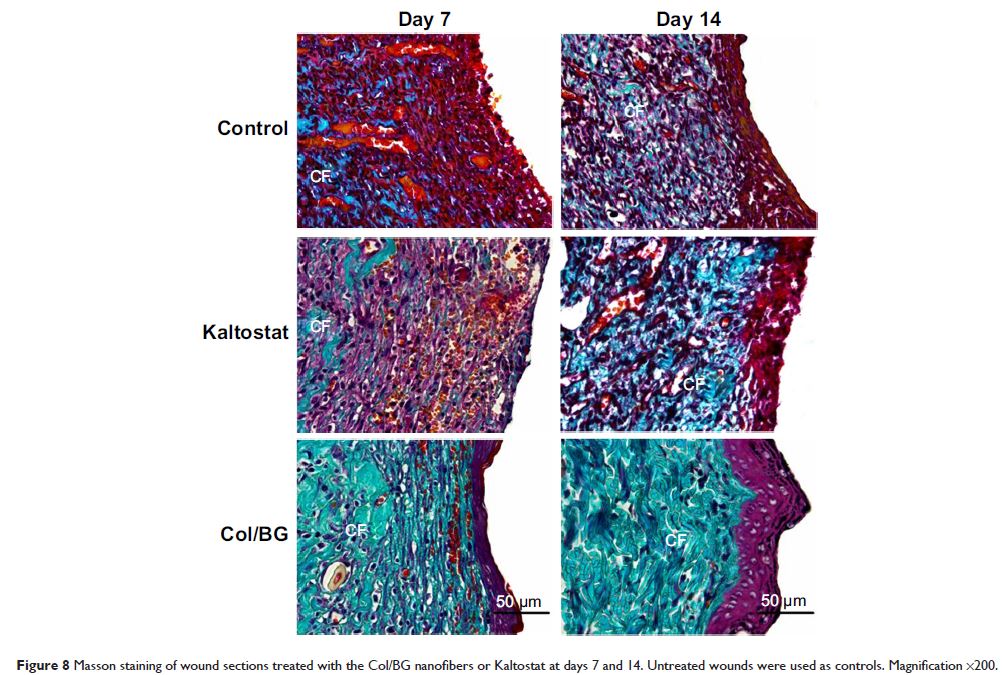
多功能和仿生鱼胶原/生物活性玻璃纳米纤维: 制备、抗菌活性和体外和体内诱导皮肤再生
Authors Zhou T, Sui B, Mo X, Sun J
Received 15 January 2017
Accepted for publication 23 March 2017
Published 2 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3495—3507
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S132459
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Bhavesh Kevadiya
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: The development of skin wound dressings with excellent properties has
always been an important challenge in the field of biomedicine. In this study,
biomimetic electrospun fish collagen/bioactive glass (Col/BG) nanofibers were
prepared. Their structure, tensile strength, antibacterial activity and
biological effects on human keratinocytes, human dermal fibroblasts and human
vascular endothelial cells were investigated. Furthermore, the Sprague Dawley
rat skin defect model was used to validate their effect on wound healing. The
results showed that compared with pure fish collagen nanofibers, the tensile
strength of the Col/BG nanofibers increased to 21.87±0.21 Mpa, with a certain
degree of antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus . It was also found that the Col/BG nanofibers promoted the adhesion,
proliferation and migration of human keratinocytes. Col/BG nanofibers induced
the secretion of type one collagen and vascular endothelial growth factor by
human dermal fibroblasts, which further stimulated the proliferation of human
vascular endothelial cells. Animal experimentation indicated that the Col/BG
nanofibers could accelerate rat skin wound healing. This study developed a type
of multifunctional and biomimetic fish Col/BG nanofibers, which had the ability
to induce skin regeneration with adequate tensile strength and antibacterial
activity. The Col/BG nanofibers are also easily available and inexpensive,
providing the possibility for using as a functional skin wound dressing.
Keywords: electrospun, collagen/bioactive glass
nanofibers, antibacterial activity, skin regeneration, angiogenesis