110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

身体质量指数与中国老年人 2 型糖尿病有关
Authors Zhao Q, Laukkanen JA, Li Q, Li G
Received 12 December 2016
Accepted for publication 3 February 2017
Published 2 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 745—752
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S130014
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: There is limited information on the association between metabolic
syndrome components including body mass index (BMI) and type 2 diabetes
mellitus in elderly Chinese population. Therefore, we investigated whether
components of metabolic syndrome are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus
in elderly.
Methods: A total of 479 hospitalized patients (aged 65–95
years) with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus were studied
retrospectively in a cross-sectional study and compared with 183 subjects with
prediabetes and 62 subjects without glucose metabolism abnormalities.
Results: BMI (24.69±3.59 versus 23.92±3.08 and 23.56±3.25 kg/m2), blood pressure, cholesterol, triglyceride, liver
enzymes and prevalence of fatty liver were higher in patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus as compared with elderly subjects with prediabetes or normal
glucose metabolism separately (all P <0.05). Multivariable
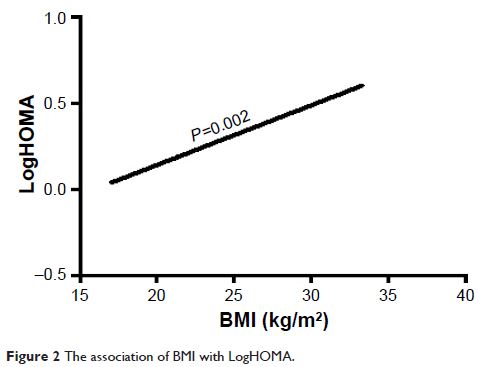
regression analysis showed that BMI was associated positively with insulin
resistance and inversely with insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus
group (all P <0.05).
Conclusion: Higher BMI was associated with increased insulin
resistance and decreased insulin sensitivity in elderly Asian population with
type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: body mass index, type 2 diabetes,
elderly, aging