110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

微管相关蛋白 Tau 蛋白与前列腺癌细胞系对多西紫杉醇 (docetaxel) 的耐药性有关
Authors Yang J, Yu Y, Liu W, Li Z, Wei ZQ, Jiang R
Received 4 August 2016
Accepted for publication 13 December 2016
Published 8 May 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 71—77
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RRU.S118966
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jan Colli
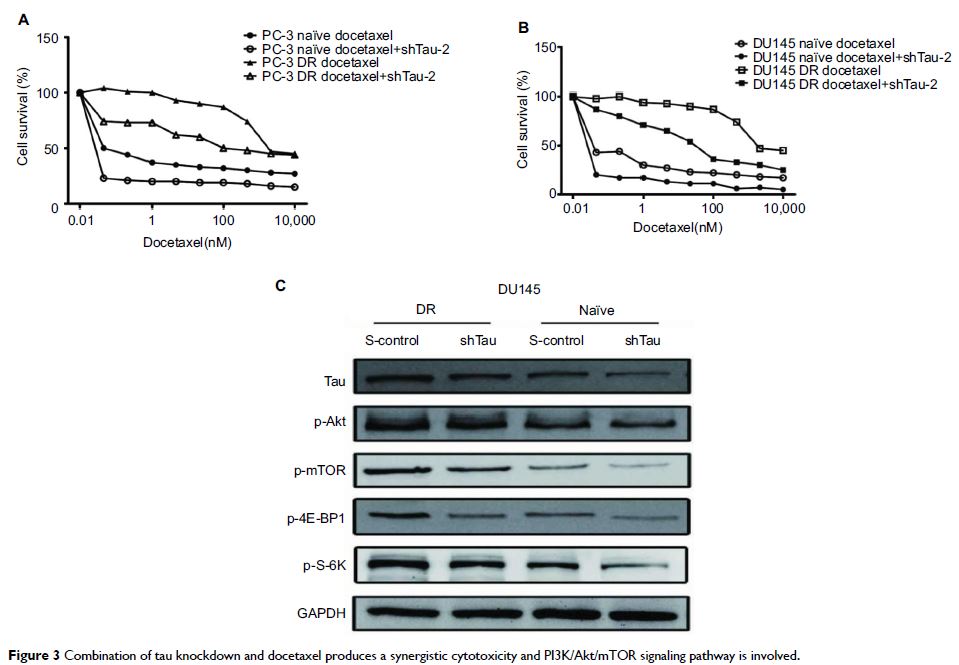
Abstract: Tau, a microtubule-associated protein, has been investigated primarily
in neurons. Recently, tau has been explored to be associated with increased
drug resistance in various kinds of cancers. We found that the tau was
expressed in prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and PC-3. We also reported that
recurrent prostate cancer cells after docetaxel treatment have higher levels of
microtubule-associated protein tau. In vitro, inactivation of tau by gene
knockdown suppressed cell proliferation and sensitized docetaxel cytotoxicity.
Also, our results demonstrated that the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway was upregulated
in DU145 docetaxel-resistant cells compared with the DU145-naïve cells. Thus,
targeting tau protein and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway are promising strategies to
enhance docetaxel response for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Keywords: prostate
cancer, microtubule-associated protein tau, docetaxel resistance, tau protein,
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway