110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肺癌中 p14ARF 表达的临床病理学意义: 一项综合分析
Authors Wang F, Li H, Long J, Ye S
Received 9 January 2017
Accepted for publication 26 March 2017
Published 8 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2491—2499
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S131954
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: p14ARF, a tumor suppressor protein, encoded by the p16
tumor suppressor gene, has been reported to be associated with the
clinicopathological features of lung cancer. However, the evaluated outcomes
were inconsistent and remained inconclusive. In this study, we conducted a
meta-analysis to clarify the significance of p14ARF expression in lung cancer
pathogenesis.
Materials and methods: Electronic databases,
PubMed, Web of Knowledge, Embase, and CNKI, were retrieved to collect relevant
articles with inclusion and exclusion criteria. Using Stata 12.0 software, 95%
confidence intervals (CIs) and odds ratios (ORs) were calculated.
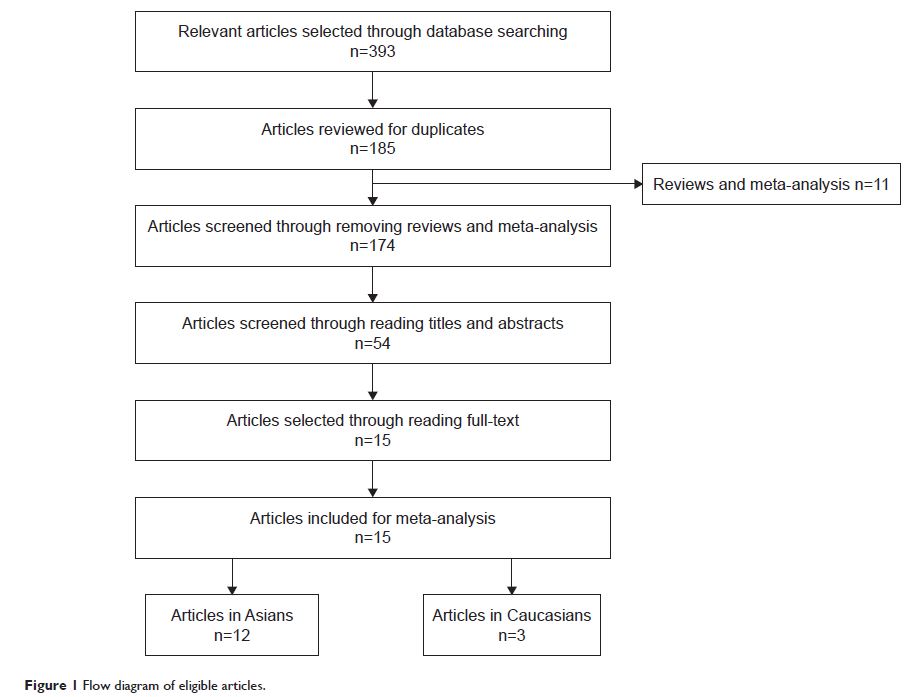
Results: A total of 15 eligible case–control studies that
evaluated the relationship between p14ARF expression and
lung cancer were included in the meta-analysis. The results demonstrated that
there were significant associations between p14ARF expression and the risk of
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), lung adenocarcinoma, and lung squamous
carcinoma (for NSCLC, OR =11.02, 95% CI =5.30–22.92; for lung
adenocarcinoma, OR =7.28, 95% CI =3.92–13.50; and for lung squamous
carcinoma, OR =14.40, 95% CI =2.83–73.24). In the stratified analysis based on
race, significant associations between p14ARF expression and lung cancer risk were
found in Chinese population and Caucasians (for Chinese population, OR = 7.02,
95% CI =4.48–11.00 and for Caucasians, OR =4.19, 95% CI =1.42–12.38).
Furthermore, the expression of p14ARF was significantly associated with the
TNM-stage of lung cancer in Chinese population (OR =2.07, 95% CI
=1.38–3.10).
Conclusion: p14ARF expression was significantly
associated with the risk of lung cancer. In addition, the data of the
meta-analysis showed that there was a significant correlation between p14ARF expression and the TNM-stage of lung cancer in
Chinese population.
Keywords: p14ARF, expression,
lung cancer, meta-analysis