110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

异常的启动子甲基化谱与肝细胞癌患者生存的关联
Authors Zhong D, Cen H
Received 18 November 2016
Accepted for publication 17 January 2017
Published 8 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2501—2509
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S128058
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Abstract: The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic and diagnostic
value of genes with promoter methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
patients. On the basis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data, we identified genes
with differentially methylated promoters in HCC tissues and adjacent non-tumor
tissues, using the linear models for microarray data approach. Cox proportional
hazard regression analysis was applied to access the prognostic value of
identified differentially methylated genes. The diagnostic value of the genes
was evaluated through receiver operating characteristic. Pathway analyses were
performed to illustrate biological functions of the identified genes. Compared
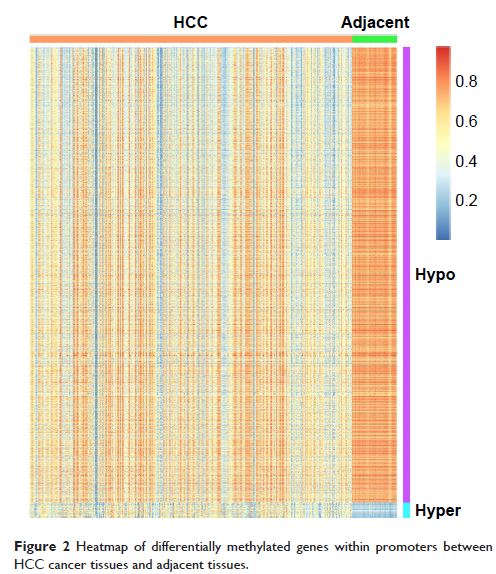
to adjacent tissues, 77 genes with hypermethylated promoters and 2,412 genes
with hypomethylated promoters were identified in HCC. The promoter
hypomethylations of RNA5SP38, IL21, SDC4P, and MIR4439 were found to be associated
with HCC patient survival (P =0.035, 0.040,
0.004, and 0.024, respectively). Hypomethylated SDC4P was associated with a
better prognosis (hazard ratio, 0.482; 95% confidence interval [CI],
-0.147–1.110; P =0.007). The
combination of the promoter hypomethylations with RNA5SP38, IL21, and SDC4P
showed an area under receiver operating characteristic curves of 0.975 (95% CI,
0.962–0.989; P =4.811E-25). Several pathways,
including olfactory transduction, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction,
natural killer cell–mediated cytotoxicity, as well as inflammation mediated by
chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway, were annotated with the
hypomethylated promoter genes. SDC4P promoter hypomethylation may be a
potential prognosis biomarker. A panel of promoter methylations in RNA5SP38,
IL21, and SDC4P was proven a novel approach to diagnosis HCC. The pathway
analysis defined the extensive functional role of DNA hypomethylation in
cancer.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, promoter
methylation, prognosis, diagnosis