110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

加载齐墩果 (Oleanolic) 酸的乳铁蛋白纳米粒子的制备、表征和体外/体内研究
Authors Xia X, Liu H, Lv H, Zhang J, Zhou JP, Zhao Z
Received 5 February 2017
Accepted for publication 5 April 2017
Published 9 May 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1417—1427
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S133997
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Rammohan Devulapally
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Abstract: Oleanolic acid (OA), a pentacyclic triterpene, is used to safely and
economically treat hepatopathy. However, OA, a Biopharmaceutics Classification
System IV category drug, has low bioavailability owing to low solubility (<1
µg/mL) and biomembrane permeability. We developed a novel OA nanoparticle
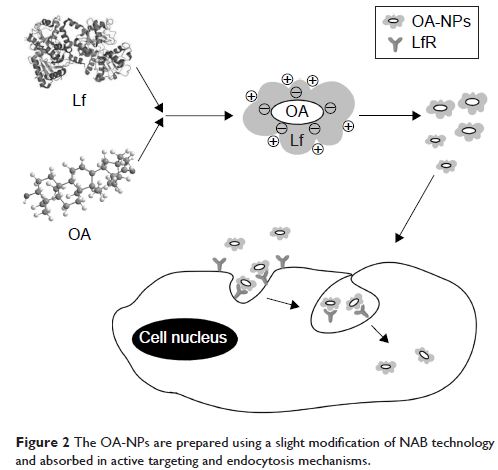
(OA-NP)-loaded lactoferrin (Lf) nanodelivery system with enhanced in vitro OA
dissolution and improved oral absorption and bioavailability. The OA-NPs were
prepared using NP albumin-bound technology and characterized using dynamic
light scattering, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray powder diffraction,
differential scanning calorimetry, and in vitro dissolution test. The in vivo
pharmacokinetics was investigated in Sprague Dawley rats using liquid
chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. OA-NPs (OA:Lf =1:6, w/w%) exhibited
spherical morphology, 202.2±8.3 nm particle size, +(27.1±0.32) mV ζ potential,
92.59%±3.24% encapsulation efficiency, and desirable in vitro release profiles.
An effective in vivo bioavailability (340.59%) was achieved compared to the
free drug following oral administration to rats. The Lf novel nanodelivery
vehicle enhanced the dissolution rate, intestinal absorption, and
bioavailability of OA. These results demonstrate that Lf NPs are a new strategy
for improving oral absorption and bioavailability of poorly soluble and poorly
absorbed drugs.
Keywords: oleanolic acid, nanoparticle,
lactoferrin nanodelivery system, drug absorption, bioavailability