110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

聚乙二醇 - 聚 (ε-苄氧羰基-L-赖氨酸) 共轭 VEGF siRNA 用于肝细胞癌抗血管生成基因治疗
Authors Wang GM, Gao XL, Gu GJ, Shao ZH, Li MH, Wang PJ, Yang JR, Cai XJ, Li YY
Received 25 December 2016
Accepted for publication 18 April 2017
Published 9 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3591—3603
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131078
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
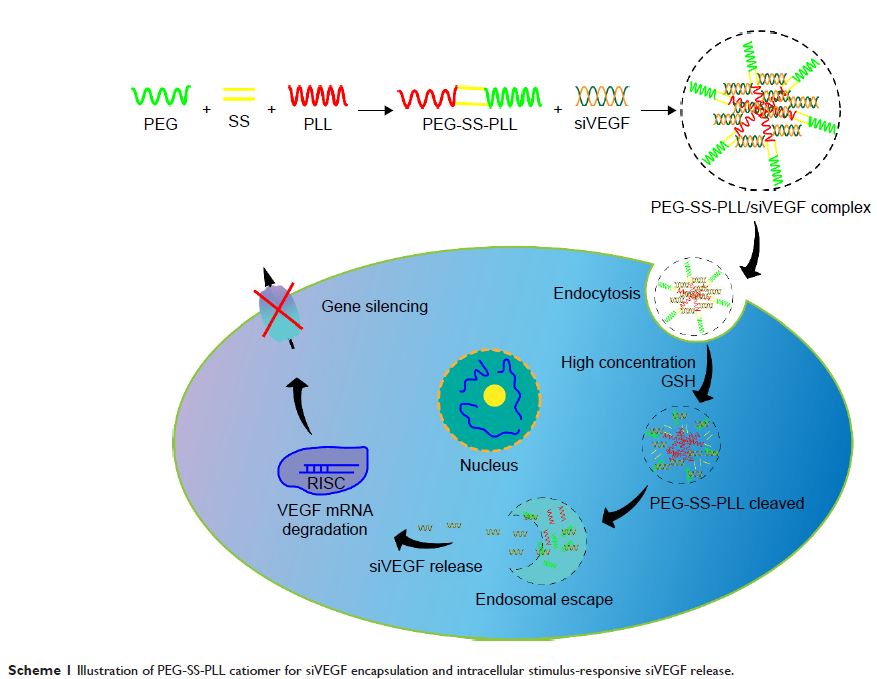
Abstract: A polyethylene glycol–poly(ε-benzyloxycarbonyl-l-lysine) (PEG-SS-PLL)
block copolymer based on a disulfide-linked, novel biodegradable catiomer
bearing a PEG-sheddable shell was developed to avoid “PEG dilemma” in
nanoparticle intracellular tracking of PEG-PLL where PEG was nondegradable.
However, PEG-SS-PLL catiomers have not been used to deliver small interfering
VEGF RNA (siVEGF) in antiangiogenesis gene therapy. In this study, we aimed to
investigate whether this novel biodegradable catiomer can deliver siVEGF into
cancer cells and at the same time have an antitumor effect in a xenograft mouse
model. It was found that PEG-SS-PLL efficiently delivered siVEGF with
negligible cytotoxicity, and significantly decreased the expression of VEGF at
both the messenger-RNA and protein levels both in vitro and in vivo, and thus
tumor growth was inhibited. Our findings demonstrated that PEG-SS-PLL/siVEGF
could potentially be applied to antiangiogenesis gene therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: polyethylene
glycol, poly lysine, disulfide, VEGF, antiangiogenesis, hepatocellular
carcinoma, siRNA