110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

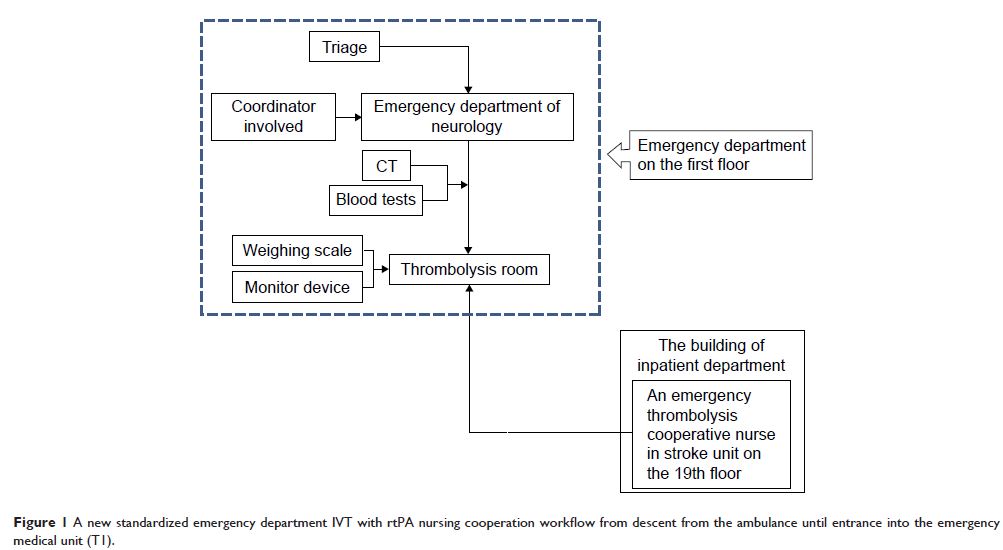
新型标准化护理合作工作流程,以减少对急性缺血性卒中患者的中风溶栓治疗的延误
Authors Zhou Y, Xu Z, Liao J, Feng F, Men L, Xu L, He Y, Li G
Received 25 November 2016
Accepted for publication 13 February 2017
Published 9 May 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1215—1220
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S128740
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Objective: We assessed the effectiveness of a new standardized nursing cooperation
workflow in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) to reduce stroke
thrombolysis delays.
Patients and
methods: AIS patients receiving conventional thrombolysis treatment from March to
September 2015 were included in the control group, referred to as T0. The
intervention group, referred to as T1 group, consisted of AIS patients
receiving a new standardized nursing cooperation workflow for intravenous
thrombolysis (IVT) at the emergency department of Shanghai East Hospital (Shanghai,
People’s Republic of China) from October 2015 to March 2016. Information was
collected on the following therapeutic techniques used: application or not of
thrombolysis, computed tomography (CT) time, and door-to-needle (DTN) time. A
nursing coordinator who helped patients fulfill the medical examinations and
diagnosis was appointed to T1 group. In addition, a nurse was sent immediately
from the stroke unit to the emergency department to aid the thrombolysis
treatment.
Results: The average value of the door-to-CT initiation time was 38.67±5.21 min
in the T0 group, whereas it was 14.39±4.35 min in the T1 group; the
average values of CT completion-to-needle time were 55.06±4.82 and
30.26±3.66 min; the average values of DTN time were 100.43±6.05 and 55.68±3.62 min,
respectively; thrombolysis time was improved from 12.8% (88/689) in the T0
group to 32.5% (231/712) in the T1 group (all P <0.01). In addition, the new
standardized nursing cooperation workflow decreased the National Institutes of
Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores at 24 h (P <0.01)
(T0: prethrombolysis, 6.97±3.98; 24 h postthrombolysis, 3.33±2.09;
2 weeks postthrombolysis, 2.25±1.01 and T1: prethrombolysis, 7.00±3.89;
24 h postthrombolysis, 2.60±1.66; 2 weeks postthrombolysis,
2.21±1.02).
Conclusion: The new standardized nursing cooperation workflow reduced stroke
thrombolysis delays in patients with AIS.
Keywords: standardization, nursing, intravenous thrombolysis, door-to-needle time,
stroke thrombolysis delay