110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Sjögren 综合征与健康有关的生活质量领域中不同的负面影响相关联:来自 36 份简短问卷调查表和一个综合分析的证据
Authors Zhang Q, Wang X, Chen H, Shen B
Received 19 January 2017
Accepted for publication 13 April 2017
Published 10 May 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 905—911
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S132751
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Purpose: The purpose of this article was to systematically review the literature
to identify the impact of primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) on specific
health-related quality of life (HRQoL) domains.
Methods: A meta-analysis was performed, and the related articles
were searched in Medline, Embase, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge
Infrastructure, China Biology Medicine, and Web of Science databases and in
reference lists of articles and systematic reviews. Score of the Short Form 36
(SF-36) questionnaire was used as the outcome measurement, and mean differences
(MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
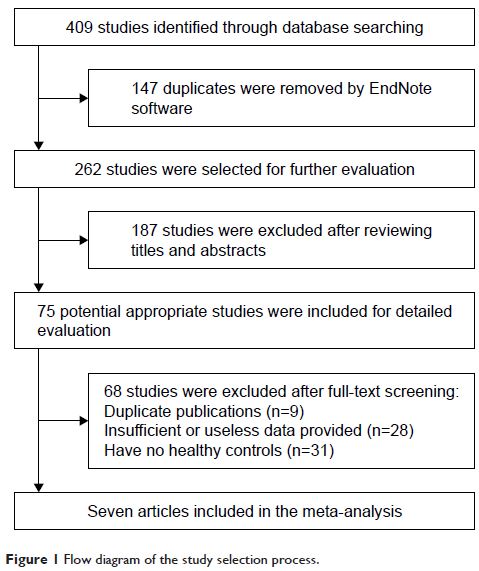
Results: Seven studies were included, comprising 521 patients
with pSS and 9,916 healthy controls. The SF-36 questionnaire score of each
domain (physical function, role physical [RP] function, emotional role
function, vitality, mental health, social function, body pain, general health,
physical component scale, mental component scale) was lower in patients with
pSS than in healthy controls, especially the score in the dimension of RP
function.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed that patients had lower pSS
score in each dimension of the SF-36, mostly in the RP function. This
demonstrated that targeted interventions should be carried out to improve the
HRQoL of pSS patients.
Keywords: primary Sjögren’s syndrome, quality of
life, SF-36, meta-analysis