110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

遗传多态性与慢性阻塞性肺病 (COPD)
Authors Yuan CH, Chang D, Lu GM, Deng XW
Received 7 February 2017
Accepted for publication 19 April 2017
Published 10 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1385—1393
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S134161
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Charles Downs
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
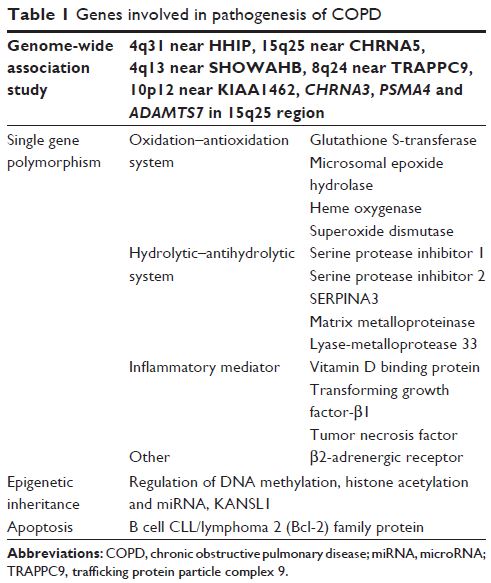
Abstract: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common chronic
disease, and its morbidity and mortality are increasing. There are many studies
that have tried to explain the pathogenesis of COPD from genetic
susceptibility, to identify the susceptibility of COPD factors, which play a
role in early prevention, early detection and the early treatment. However, it
is well known that COPD is an inflammatory disease characterized by incomplete
reversible airflow limitation in which genes interact with the environment. In
recent years, many studies have proved gene polymorphisms and COPD correlation.
However, there is less research on the relationship between COPD and
genome-wide association study (GWAS), epigenetics and apoptosis. In this paper,
we summarized the correlation between gene level and COPD from the following
four aspects: the GWAS, the gene polymorphism, the epigenetics and the
apoptosis, and the relationship between COPD and gene is summarized
comprehensively.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,
COPD, genetic polymorphism, genome-wide association study